Neuronal activity-regulated gene transcription in synapse development and cognitive function
- PMID: 21555405
- PMCID: PMC3098681
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005744
Neuronal activity-regulated gene transcription in synapse development and cognitive function
Abstract
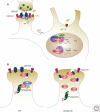
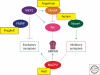
Activity-dependent plasticity of vertebrate neurons allows the brain to respond to its environment. During brain development, both spontaneous and sensory-driven neural activity are essential for instructively guiding the process of synapse development. These effects of neuronal activity are transduced in part through the concerted regulation of a set of activity-dependent transcription factors that coordinate a program of gene expression required for the formation and maturation of synapses. Here we review the cellular signaling networks that regulate the activity of transcription factors during brain development and discuss the functional roles of specific activity-regulated transcription factors in specific stages of synapse formation, refinement, and maturation. Interestingly, a number of neurodevelopmental disorders have been linked to abnormalities in activity-regulated transcriptional pathways, indicating that these signaling networks are critical for cognitive development and function.
Figures


References
-
- Adams JP, Dudek SM 2005. Late-phase long-term potentiation: Getting to the nucleus. Nat Rev Neurosci 6: 737–743 - PubMed
-
- Aizawa H, Hu SC, Bobb K, Balakrishnan K, Ince G, Gurevich I, Cowan M, Ghosh A 2004. Dendrite development regulated by CREST, a calcium-regulated transcriptional activator. Science 303: 197–202 - PubMed
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY 1999. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet 23: 185–188 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DD 2005. Neuropathology of Rett syndrome. J Child Neurol 20: 747–753 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
