Exploring the inhibition of CTX-M-9 by beta-lactamase inhibitors and carbapenems
- PMID: 21555770
- PMCID: PMC3122419
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00089-11
Exploring the inhibition of CTX-M-9 by beta-lactamase inhibitors and carbapenems
Abstract
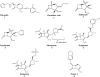
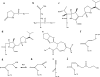
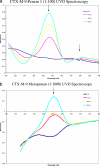
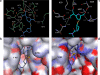
Currently, CTX-M β-lactamases are among the most prevalent and most heterogeneous extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs). In general, CTX-M enzymes are susceptible to inhibition by β-lactamase inhibitors. However, it is unknown if the pathway to inhibition by β-lactamase inhibitors for CTX-M ESBLs is similar to TEM and SHV β-lactamases and why bacteria possessing only CTX-M ESBLs are so susceptible to carbapenems. Here, we have performed a kinetic analysis and timed electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) studies to reveal the intermediates of inhibition of CTX-M-9, an ESBL representative of this family of enzymes. CTX-M-9 β-lactamase was inactivated by sulbactam, tazobactam, clavulanate, meropenem, doripenem, ertapenem, and a 6-methylidene penem, penem 1. K(i) values ranged from 1.6 ± 0.3 μM (mean ± standard error) for tazobactam to 0.02 ± 0.01 μM for penem 1. Before and after tryptic digestion of the CTX-M-9 β-lactamase apo-enzyme and CTX-M-9 inactivation by inhibitors (meropenem, clavulanate, sulbactam, tazobactam, and penem 1), ESI-MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) identified different adducts attached to the peptide containing the active site Ser70 (+52, 70, 88, and 156 ± 3 atomic mass units). This study shows that a multistep inhibition pathway results from modification or fragmentation with clavulanate, sulbactam, and tazobactam, while a single acyl enzyme intermediate is detected when meropenem and penem 1 inactivate CTX-M-9 β-lactamase. More generally, we propose that Arg276 in CTX-M-9 plays an essential role in the recognition of the C(3) carboxylate of inhibitors and that the localization of this positive charge to a "region of the active site" rather than a specific residue represents an important evolutionary strategy used by β-lactamases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of OXA-1 beta-lactamase by penems.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Sep;52(9):3135-43. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01677-07. Epub 2008 Jun 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18559643 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor resistance in the KPC-2 beta-lactamase, a preeminent property of this class A beta-lactamase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Feb;54(2):890-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00693-09. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20008772 Free PMC article.
-
Penicillanic Acid Sulfones Inactivate the Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase CTX-M-15 through Formation of a Serine-Lysine Cross-Link: an Alternative Mechanism of β-Lactamase Inhibition.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0179321. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01793-21. Epub 2022 May 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35612361 Free PMC article.
-
Cefotaximases (CTX-M-ases), an expanding family of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases.Can J Microbiol. 2004 Mar;50(3):137-65. doi: 10.1139/w03-111. Can J Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15105882 Review.
-
Imipenem-Relebactam and Meropenem-Vaborbactam: Two Novel Carbapenem-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations.Drugs. 2018 Jan;78(1):65-98. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0851-9. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29230684 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational Intermediate That Controls KPC-2 Catalysis and Beta-Lactam Drug Resistance.ACS Catal. 2018 Apr 6;8(4):2741-2747. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b03832. Epub 2018 Feb 21. ACS Catal. 2018. PMID: 30637173 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Analysis of The OXA-48 Carbapenemase Bound to A "Poor" Carbapenem Substrate, Doripenem.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Sep 11;8(3):145. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8030145. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31514291 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in silico β-lactamase inhibitory properties and phytochemical profile of Ocimum basilicum cultivated in central delta of Egypt.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1969-1980. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2127791. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 36226757 Free PMC article.
-
Boronic Acid Transition State Inhibitors Active against KPC and Other Class A β-Lactamases: Structure-Activity Relationships as a Guide to Inhibitor Design.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jan 4;60(3):1751-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02641-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26729496 Free PMC article.
-
LN-1-255, a penicillanic acid sulfone able to inhibit the class D carbapenemase OXA-48.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Aug;71(8):2171-80. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw105. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27125555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown R. P., Aplin R. T., Schofield C. J. 1996. Inhibition of TEM-2 β-lactamase from Escherichia coli by clavulanic acid: observation of intermediates by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 35:12421–12432 - PubMed
-
- Bulychev A., Massova I., Lerner S. A., Mobashery S. 1995. Penem BRL 42715: an effective inactivator for β-lactamases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117:4797–4801
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

