Amyloid precursor protein is trafficked and secreted via synaptic vesicles
- PMID: 21556148
- PMCID: PMC3083403
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018754
Amyloid precursor protein is trafficked and secreted via synaptic vesicles
Abstract
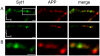
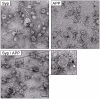
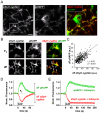
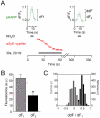
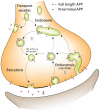
A large body of evidence has implicated amyloid precursor protein (APP) and its proteolytic derivatives as key players in the physiological context of neuronal synaptogenesis and synapse maintenance, as well as in the pathology of Alzheimer's Disease (AD). Although APP processing and release are known to occur in response to neuronal stimulation, the exact mechanism by which APP reaches the neuronal surface is unclear. We now demonstrate that a small but relevant number of synaptic vesicles contain APP, which can be released during neuronal activity, and most likely represent the major exocytic pathway of APP. This novel finding leads us to propose a revised model of presynaptic APP trafficking that reconciles existing knowledge on APP with our present understanding of vesicular release and recycling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Sisodia SS, Price DL. Role of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 1995;9:366–370. - PubMed
-
- Bell KF, Zheng L, Fahrenholz F, Cuello AC. ADAM-10 over-expression increases cortical synaptogenesis. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:554–565. - PubMed
-
- De Strooper B, Saftig P, Craessaerts K, Vanderstichele H, Guhde G, et al. Deficiency of presenilin-1 inhibits the normal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. Nature. 1998;391:387–390. - PubMed
-
- Cirrito JR, Yamada KA, Finn MB, Sloviter RS, Bales KR, et al. Synaptic activity regulates interstitial fluid amyloid-beta levels in vivo. Neuron. 2005;48:913–922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

