Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned?
- PMID: 21556860
- PMCID: PMC3132380
- DOI: 10.1007/s00251-011-0528-6
Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned?
Abstract
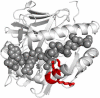
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting 0.5-1% of the population worldwide. The disease has a heterogeneous character, including clinical subsets of anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive and APCA-negative disease. Although the pathogenesis of RA is poorly understood, progress has been made in identifying genetic factors that contribute to the disease. The most important genetic risk factor for RA is found in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) locus. In particular, the HLA molecules carrying the amino acid sequence QKRAA, QRRAA, or RRRAA at positions 70-74 of the DRβ1 chain are associated with the disease. The HLA molecules carrying these "shared epitope" sequences only predispose for ACPA-positive disease. More than two decades after the discovery of HLA-DRB1 as a genetic risk factor, the second genetic risk factor for RA was identified in 2003. The introduction of new techniques, such as methods to perform genome-wide association has led to the identification of more than 20 additional genetic risk factors within the last 4 years, with most of these factors being located near genes implicated in immunological pathways. These findings underscore the role of the immune system in RA pathogenesis and may provide valuable insight into the specific pathways that cause RA.
Figures
References
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Menard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barton A, Thomson W, Ke X, Eyre S, Hinks A, Bowes J, Plant D, Gibbons LJ, Wilson AG, Bax DE, Morgan AW, Emery P, Steer S, Hocking L, Reid DM, Wordsworth P, Harrison P, Worthington J. Rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility loci at chromosomes 10p15, 12q13 and 22q13. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1156–1159. doi: 10.1038/ng.218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Begovich AB, Carlton VE, Honigberg LA, Schrodi SJ, Chokkalingam AP, Alexander HC, Ardlie KG, Huang Q, Smith AM, Spoerke JM, Conn MT, Chang M, Chang SY, Saiki RK, Catanese JJ, Leong DU, Garcia VE, McAllister LB, Jeffery DA, Lee AT, Batliwalla F, Remmers E, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Kastner DL, Amos CI, Sninsky JJ, Gregersen PK. A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:330–337. doi: 10.1086/422827. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

