Prospective multi-arm evaluation of surgical treatments for vocal fold scar and pathologic sulcus vocalis
- PMID: 21557241
- PMCID: PMC3100420
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.21780
Prospective multi-arm evaluation of surgical treatments for vocal fold scar and pathologic sulcus vocalis
Abstract
Objectives/hypothesis: The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical effectiveness of type I thyroplasty, injection laryngoplasty, and graft implantation for the treatment of vocal fold scar and pathologic sulcus vocalis.
Study design: Prospective, multi-arm, quasi-experimental research design.
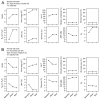
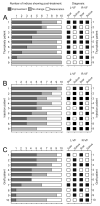
Methods: Twenty-eight patients with newly diagnosed vocal fold scar and/or pathologic sulcus vocalis were assigned to one of three treatment modalities: type I thyroplasty (n = 9), injection laryngoplasty (n = 9), and graft implantation (n = 10). Psychosocial, auditory-perceptual, acoustic, aerodynamic, and videostroboscopic data were collected pretreatment and at 1, 6, 12, and 18 months posttreatment.
Results: Type I thyroplasty and graft implantation both resulted in reduced voice handicap with no concomitant improvement in auditory-perceptual, acoustic, aerodynamic, or vocal fold physiologic performance. Injection laryngoplasty resulted in no improvement on any vocal function index. Patients who underwent graft implantation exhibited the slowest improvement trajectory across the 18-month follow-up period.
Conclusions: A persistent challenge in this area is that no single treatment modality is successful for the majority of patients, and there is no evidence-based decision algorithm for matching a given treatment to a given patient. Progress therefore requires the identification and categorization of predictive clinical features that can drive evidence-based treatment assignment.
Copyright © 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological, and Otological Society, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hold no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hirano S, Minamiguchi S, Yamashita M, Ohno T, Kanemaru S, Kitamura M. Histologic characterization of human scarred vocal folds. J Voice. 2009;23:399–407. - PubMed
-
- Thibeault SL, Gray SD, Bless DM, Chan RW, Ford CN. Histologic and rheologic characterization of vocal fold scarring. J Voice. 2002;16:96–104. - PubMed
-
- Rousseau B, Hirano S, Scheidt TD, et al. Characterization of vocal fold scarring in a canine model. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:620–627. - PubMed
-
- Hirano M, Yoshida T, Tanaka S, Hibi S. Sulcus vocalis: functional aspects. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990;99:679–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

