Gender-related differences in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction: results from the registry study of the ST elevation myocardial infarction network Essen
- PMID: 21557255
- PMCID: PMC6652718
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.20916
Gender-related differences in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction: results from the registry study of the ST elevation myocardial infarction network Essen
Abstract
Background: The Myocardial Infarction Network Essen was initiated in order to establish a standardized procedure with immediate reopening of the infarcted vessel for patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in the city of Essen, Germany. The present study aims to evaluate gender-related differences in presentation of disease and clinical outcome.
Hypothesis: Gender is associated with differences in presentation and outcome of STEMI.
Methods: All patients with STEMI were included without exception. Parameters such as risk profile, mortality, and relevant time intervals were documented. The follow-up period was 1 year.
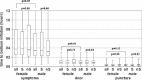
Results: For this study, 1365 patients (72.1% male) were recruited. Women were significantly older, with higher prevalence of diabetes (28.1% vs 20.3%, P = 0.004) and hypertension (76.5% vs 64.8%, P<0.0005). Analysis of time intervals between symptoms to actions showed no significant differences. However, women tended to wait longer before calling for medical assistance (358 vs 331 min, P = 0.091). In-hospital mortality was comparable with respect to gender, whereas women had higher 1-year mortality (18.6% vs 13.2%). Age and diabetes were associated with a higher mortality. Adjusted for age, gender is no longer an independent risk factor. In the follow-up period, significantly more women were readmitted to the hospital without a difference in the frequency of reangiography, surgery, or target-vessel revascularization.
Conclusions: The present data display a successful implementation of a standardized procedure in patients with STEMI. Although differences between genders are not as obvious as expected, efforts should be taken to perform a gender-specific risk analysis as well as to promote education about proper behavior in case of new onset of angina.
2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Suessenbacher A, Doerler J, Alber H, et al. Gender‐related outcome following percutaneous coronary intervention for ST‐elevation myocardial infarction: data from the Austrian acute PCI registry. EuroIntervention. 2008;4:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Srichaiveth B, Ruengsakulrach P, Visudharom K, et al. Impact of gender on treatment and clinical outcomes in acute ST elevation myocardial infarction patients in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(suppl 1): 65–73. - PubMed
-
- Hvelplund A, Galatius S, Madsen M, et al. Women with acute coronary syndrome are less invasively examined and subsequently less treated than men. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:684–690. - PubMed
-
- Wake R, Yoshiyama M. Gender differences in ischemic heart disease. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2009;4:234–240. - PubMed
-
- The GUSTO Investigators . An international randomized trial comparing four thrombolytic strategies for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:673–682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

