VS-105: a novel vitamin D receptor modulator with cardiovascular protective effects
- PMID: 21557735
- PMCID: PMC3188908
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01473.x
VS-105: a novel vitamin D receptor modulator with cardiovascular protective effects
Abstract
Background and purpose: Vitamin D receptor (VDR) modulators (VDRMs) such as calcitriol, paricalcitol and doxercalciferol are commonly used to manage hyperparathyroidism secondary to chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD patients experience extremely high risks of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Clinical observations show that VDRM therapy may be associated with cardio-renal protective and survival benefits for CKD patients. However, hypercalcaemia remains a serious side effect for current VDRMs, which leads to the need for frequent dose titration and serum Ca (calcium) monitoring. Significant clinical benefits can be derived from a VDRM with cardiovascular protective effects without the hypercalcaemic liability.
Experimental approach: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were 5/6 nephrectomized and 6 weeks later, after they had established uraemia, elevated parathyroid hormone levels, endothelial dysfunction and left ventricular hypertrophy, the rats were treated with VS-105, a novel VDRM. The effects of VS-105 were also tested in cultured HL-60 cells.
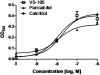
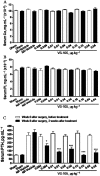
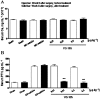
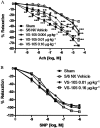
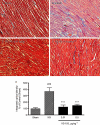
Key results: VS-105 induced HL-60 cell differentiation with an EC₅₀ value at 11.8 nM. Treatment (i.p., 3× a week over a period of 2 weeks) of the 5/6 nephrectomized rats by VS-105 (0.004-0.64 µg·kg⁻¹) effectively suppressed serum parathyroid hormone without raising serum Ca or phosphate levels. Furthermore, 2 weeks of treatment with VS-105 improved endothelium-dependent aortic relaxation and attenuated left ventricular abnormalities in a dose range that did not affect serum Ca levels. Similar results were obtained when VS-105 was administered i.p. or by oral gavage.
Conclusions and implications: VS-105 exhibits an overall therapeutic product profile that supports expanded use in CKD to realize the cardiovascular protective effects of VDR activation.
© 2011 Vidasym. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
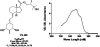
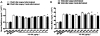
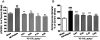
References
-
- Agarwal R, Acharya M, Tian J, Hippensteel RL, Melnick JZ, Qiu P, et al. Antiproteinuric effect of oral paricalcitol in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005;68:2823–2828. - PubMed
-
- Alborzi P, Patel NA, Peterson C, Bills JE, Bekele DM, Bunaye Z, et al. Paricalcitol reduces albuminuria and inflammation in chronic kidney disease: a randomized double-blind pilot trial. Hypertension. 2008;52:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Burbury K, Wheeler D. Premature cardiovascular disease in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 2000;356:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Biggar PH, Liangos O, Fey H, Brandenburg VM, Ketteler M. Vitamin D, chronic kidney disease and survival: a pluripotent hormone or just another bone drug? Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:7–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

