The flavonoid scaffold as a template for the design of modulators of the vascular Ca(v) 1.2 channels
- PMID: 21557738
- PMCID: PMC3230815
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01476.x
The flavonoid scaffold as a template for the design of modulators of the vascular Ca(v) 1.2 channels
Abstract
Background and purpose: Previous studies have pointed to the plant flavonoids myricetin and quercetin as two structurally related stimulators of vascular Ca(v) 1.2 channel current (I(Ca1.2) ). Here we have tested the proposition that the flavonoid structure confers the ability to modulate Ca(v) 1.2 channels.
Experimental approach: Twenty-four flavonoids were analysed for their effects on I(Ca1.2) in rat tail artery myocytes, using the whole-cell patch-clamp method.
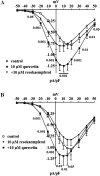
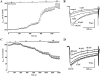
Key results: Most of the flavonoids stimulated or inhibited I(Ca1.2) in a concentration- and voltage-dependent manner with EC(50) values ranging between 4.4 µM (kaempferol) and 16.0 µM (myricetin) for the stimulators and IC(50) values between 13.4 µM (galangin) and 100 µM [(±)-naringenin] for the inhibitors. Key structural requirements for I(Ca1.2) stimulatory activity were the double bond between C2 and C3 and the hydroxylation pattern on the flavonoid scaffold, the latter also determining the molecular charge, as shown by molecular modelling techniques. Absence of OH groups in the B ring was key in I(Ca1.2) inhibition. The functional interaction between quercetin and either the stimulator myricetin or the antagonists resokaempferol, crysin, genistein, and 5,7,2'-trihydroxyflavone revealed that quercetin expressed the highest apparent affinity, in the low µM range, for Ca(v) 1.2 channels. Neither protein tyrosine kinase nor protein kinase Cα were involved in quercetin-induced stimulation of I(Ca1.2).
Conclusions and implications: Quercetin-like plant flavonoids were active on vascular Ca(v)1.2 channels. Thus, the flavonoid scaffold may be a template for the design of novel modulators of vascular smooth muscle Ca(v)1.2 channels, valuable for the treatment of hypertension and stroke.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


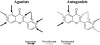
References
-
- Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, Ogawara H, Watanabe S, Itoh N, et al. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:5592–5595. - PubMed
-
- Carosati E, Sforna G, Pippi M, Marverti G, Ligabue A, Guerrieri D, et al. Ligand-based virtual screening and ADME-tox guided approach to identify triazolo-quinoxalines as folate cycle inhibitors. Bioorgan Med Chem. 2010;18:7773–7785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

