Panic disorder and its subtypes: a comprehensive analysis of panic symptom heterogeneity using epidemiological and treatment seeking samples
- PMID: 21557895
- PMCID: PMC4096693
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291711000547
Panic disorder and its subtypes: a comprehensive analysis of panic symptom heterogeneity using epidemiological and treatment seeking samples
Abstract
Background: Panic disorder (PD) is a heterogeneous syndrome that can present with a variety of symptom profiles that potentially reflect distinct etiologic pathways. The present study represents the most comprehensive examination of phenotypic variance in PD with and without agoraphobia for the purpose of identifying clinically relevant and etiologically meaningful subtypes.
Method: Latent class (LC) and factor mixture analysis were used to examine panic symptom data ascertained from three national epidemiologic surveys [Epidemiological Catchment Area (ECA), National Comorbidity Study (NCS), National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC), Wave 1], a twin study [Virginia Adult Twin Study of Psychiatric and Substance Use Disorders (VATSPSUD)] and a clinical trial (Cross-National Collaborative Panic Study [CNCPS]).
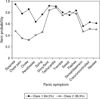
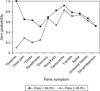
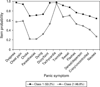
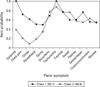
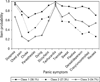
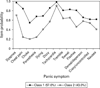
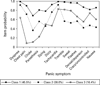
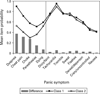
Results: Factor mixture models (versus LC) generally provided better fit to panic symptom data and suggested two panic classes for the ECA, VATSPSUD and CNCPS, with one class typified by prominent respiratory symptoms. The NCS yielded two classes, but suggested both qualitative and quantitative differences. The more contemporary NESARC sample supported a two and three class model, with the three class model suggesting two variants of respiratory panic. The NESARC's three class model continued to provide the best fit when the model was restricted to a more severe form of PD/panic disorder with agoraphobia.
Conclusions: Results from epidemiologic and clinical samples suggest two panic subtypes, with one subtype characterized by a respiratory component and a second class typified by general somatic symptoms. Results are discussed in light of their relevance to the etiopathogenesis of PD.
Figures
References
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd edn revised. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1987.
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th edn revised. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Briggs AC, Stretch DD, Brandon S. Subtyping of panic disorder by symptom profile. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1993;163:201–209. - PubMed
-
- CNCPS. Drug treatment of panic disorder : comparative efficacy of alprazolam, imipramine, and placebo. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1992;160:191–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

