Modeling the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) outbreaks throughout the hospitals in Orange County, California
- PMID: 21558768
- PMCID: PMC3388111
- DOI: 10.1086/660014
Modeling the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) outbreaks throughout the hospitals in Orange County, California
Erratum in
- Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011 Sep;32(9):938
Abstract
Background: Since hospitals in a region often share patients, an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in one hospital could affect other hospitals.
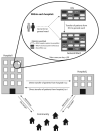
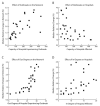
Methods: Using extensive data collected from Orange County (OC), California, we developed a detailed agent-based model to represent patient movement among all OC hospitals. Experiments simulated MRSA outbreaks in various wards, institutions, and regions. Sensitivity analysis varied lengths of stay, intraward transmission coefficients (β), MRSA loss rate, probability of patient transfer or readmission, and time to readmission.
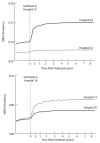
Results: Each simulated outbreak eventually affected all of the hospitals in the network, with effects depending on the outbreak size and location. Increasing MRSA prevalence at a single hospital (from 5% to 15%) resulted in a 2.9% average increase in relative prevalence at all other hospitals (ranging from no effect to 46.4%). Single-hospital intensive care unit outbreaks (modeled increase from 5% to 15%) caused a 1.4% average relative increase in all other OC hospitals (ranging from no effect to 12.7%).
Conclusion: MRSA outbreaks may rarely be confined to a single hospital but instead may affect all of the hospitals in a region. This suggests that prevention and control strategies and policies should account for the interconnectedness of health care facilities.
Figures



References
-
- McDonald JR, Carriker CM, Pien BC, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus outbreak in an intensive care nursery: potential for interinstitutional spread. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26(8):678–683. - PubMed
-
- Widerstrom M, Monsen T, Karlsson C, Wistrom J. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in a Swedish county hospital: evidence of intra- and interhospital clonal spread. J Hosp Infect. 2006;64:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Garcia M, De la Torre MA, Morales G, et al. Clinical outbreak of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an intensive care unit. JAMA. 2010;303(22):2260–2264. - PubMed
-
- Ludlam HA, Swayne RL, Kearns AM, et al. Evidence from a UK teaching hospital that MRSA is primarily transmitted by the hands of healthcare workers. J Hosp Infect. 2010;74(3):296–299. - PubMed
-
- van Rijen MM, Bosch T, Heck ME, Kluytman JA. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology and transmission in a Dutch hospital. J Hosp Infect. 2009;72(4):299–306. - PubMed
