Method for deriving visual field boundaries from OCT scans of patients with retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 21559123
- PMCID: PMC3087568
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.2.001106
Method for deriving visual field boundaries from OCT scans of patients with retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
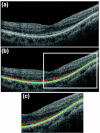
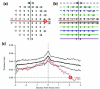
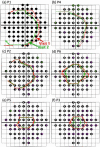
The location of the loss of the inner segment (IS)/outer segment (OS) border, as seen with frequency domain optical coherence tomography (fdOCT), was determined on fdOCT scans from patients with retinitis pigmentosa. A comparison to visual field loss supported the hypothesis, based upon previous work, that the point at which the IS/OS border disappears provides a structural marker for the edge of the visual field. Repeat fdOCT measures showed good within day reproducibility, while data obtained on average 22.5 months later showed signs of progression. The IS/OS contour shows promise as a measure for following changes in patients undergoing treatment.
Keywords: (170.4500) Optical coherence tomography; (330.4300) Vision system - noninvasive assessment.
Figures


References
-
- Aleman T. S., Cideciyan A. V., Sumaroka A., Windsor E. A., Herrera W., White D. A., Kaushal S., Naidu A., Roman A. J., Schwartz S. B., Stone E. M., Jacobson S. G., “Retinal laminar architecture in human retinitis pigmentosa caused by Rhodopsin gene mutations,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49(4), 1580–1590 (2008).10.1167/iovs.07-1110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jacobson S. G., Aleman T. S., Sumaroka A., Cideciyan A. V., Roman A. J., Windsor E. A., Schwartz S. B., Rehm H. L., Kimberling W. J., “Disease boundaries in the retina of patients with Usher syndrome caused by MYO7A gene mutations,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50(4), 1886–1894 (2009).10.1167/iovs.08-3122 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacobson S. G., Cideciyan A. V., Aleman T. S., Sumaroka A., Windsor E. A., Schwartz S. B., Heon E., Stone E. M., “Photoreceptor layer topography in children with leber congenital amaurosis caused by RPE65 mutations,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49(10), 4573–4577 (2008).10.1167/iovs.08-2121 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
