Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 21560073
- PMCID: PMC3142546
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0689-3
Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles
Abstract
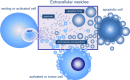
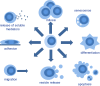
Release of membrane vesicles, a process conserved in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, represents an evolutionary link, and suggests essential functions of a dynamic extracellular vesicular compartment (including exosomes, microparticles or microvesicles and apoptotic bodies). Compelling evidence supports the significance of this compartment in a broad range of physiological and pathological processes. However, classification of membrane vesicles, protocols of their isolation and detection, molecular details of vesicular release, clearance and biological functions are still under intense investigation. Here, we give a comprehensive overview of extracellular vesicles. After discussing the technical pitfalls and potential artifacts of the rapidly emerging field, we compare results from meta-analyses of published proteomic studies on membrane vesicles. We also summarize clinical implications of membrane vesicles. Lessons from this compartment challenge current paradigms concerning the mechanisms of intercellular communication and immune regulation. Furthermore, its clinical implementation may open new perspectives in translational medicine both in diagnostics and therapy.
Figures




References
-
- van der Pol E, Hoekstra AG, Sturk A, Otto C, van Leeuwen TG, Nieuwland R. Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(12):2596–2607. - PubMed
-
- Islam A, Jones H, Hiroi T, Lam J, Zhang J, Moss J, Vaughan M, Levine SJ. cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling induces TNFR1 exosome-like vesicle release via anchoring of PKA regulatory subunit RIIbeta to BIG2. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(37):25364–25371. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804966200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

