Pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial comparing local infiltration anesthesia and continuous femoral block
- PMID: 21561303
- PMCID: PMC3237035
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2011.581264
Pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial comparing local infiltration anesthesia and continuous femoral block
Abstract
Background and purpose: Pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is usually severe, and epidural analgesia or femoral nerve block has been considered to be an effective pain treatment. Recently, local infiltration analgesia (LIA) has become increasingly popular but the outcome of this method regarding the analgesic effect has not been fully evaluated. We compared local infiltration analgesia and femoral block with regard to analgesia and morphine demand during the first 24 h after TKA.
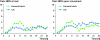
Methods: 40 patients undergoing TKA under spinal anesthesia were randomized to receive femoral nerve block (group F) or peri- and intraarticular infiltration analgesia (group LIA) with a mixture containing ropivacaine, ketorolac, and epinephrine. All patients had access to intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) with morphine postoperatively. Pain intensity at rest and upon movement was assessed on a numeric rating scale (0-10) on an hourly basis over 24 h if the patients were awake.
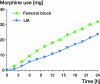
Results: The average pain at rest was marginally lower with LIA (1.6) than with femoral block (2.2). Total morphine consumption per kg was similar between the 2 groups. Ancillary analysis revealed that 1 of 20 patients in the LIA group reported a pain intensity of > 7 upon movement, as compared to 7 out of 19 in the femoral block group (p = 0.04).
Interpretation: Both LIA and femoral block provide good analgesia after TKA. LIA may be considered to be superior to femoral block since it is cheaper and easier to perform.
Figures
References
-
- Afzal A, Hawkins F, Rosenquist RW. Epidural hematoma in a patient receiving epidural analgesia and LMWH after total-knee arthroplasty. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2006;31(5):480. - PubMed
-
- Andersen LO, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H. High-volume infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008a;52(10):1331–5. - PubMed
-
- Andersen LO, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H. A compression bandage improves local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2008b;79(6):806–11. - PubMed
-
- Ben-David B, Katz E, Gaitini L, Goldik Z. Comparison of i.m. and local infiltration of ketorolac with and without local anaesthetic. Br J Anaesth. 1995;75(4):409–12. - PubMed
-
- Busch CA, Shore BJ, Bhandari R, Ganapathy S, MacDonald SJ, Bourne RB, et al. Efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection in total knee arthroplasty. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2006;88(5):959–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical