Evidence for human lung stem cells
- PMID: 21561345
- PMCID: PMC3197695
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1101324
Evidence for human lung stem cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Kajstura J et al. Evidence for Human Lung Stem Cells. N Engl J Med 2011;364:1795-806.N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 8;379(19):1870. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1813802. Epub 2018 Oct 17. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30332555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Although progenitor cells have been described in distinct anatomical regions of the lung, description of resident stem cells has remained elusive.
Methods: Surgical lung-tissue specimens were studied in situ to identify and characterize human lung stem cells. We defined their phenotype and functional properties in vitro and in vivo.
Results: Human lungs contain undifferentiated human lung stem cells nested in niches in the distal airways. These cells are self-renewing, clonogenic, and multipotent in vitro. After injection into damaged mouse lung in vivo, human lung stem cells form human bronchioles, alveoli, and pulmonary vessels integrated structurally and functionally with the damaged organ. The formation of a chimeric lung was confirmed by detection of human transcripts for epithelial and vascular genes. In addition, the self-renewal and long-term proliferation of human lung stem cells was shown in serial-transplantation assays.
Conclusions: Human lungs contain identifiable stem cells. In animal models, these cells participate in tissue homeostasis and regeneration. They have the undemonstrated potential to promote tissue restoration in patients with lung disease. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health.).
Figures

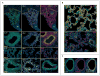

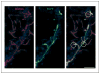
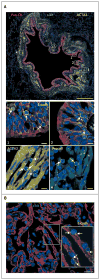
Comment in
-
Toward lung regeneration.N Engl J Med. 2011 May 12;364(19):1867-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1101800. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21561353 No abstract available.
-
Evidence for human lung stem cells.N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug 4;365(5):465; author reply 465-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1106693. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21812678 No abstract available.
-
Evidence for human lung stem cells.N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug 4;365(5):464-5; author reply 465-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1106693. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21812679 No abstract available.
-
Evidence for human lung stem cells.N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug 4;365(5):464; author reply 465-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1106693. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21812680 No abstract available.
-
Human lung stem cells: oh, the places you'll go!EMBO Mol Med. 2011 Oct;3(10):575-7. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100166. Epub 2011 Aug 19. EMBO Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21853530 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kotton DN, Fine A. Lung stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331:145–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
