Hydrophobic motif phosphorylation is not required for activation loop phosphorylation of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1)
- PMID: 21561857
- PMCID: PMC3123118
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.258004
Hydrophobic motif phosphorylation is not required for activation loop phosphorylation of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1)
Abstract
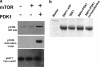
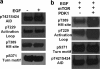
p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) is regulated by multiple phosphorylation events. Three of these sites are highly conserved among AGC kinases (cAMP dependent Protein Kinase, cGMP dependent Protein Kinase, and Protein Kinase C subfamily): the activation loop in the kinase domain, and two C-terminal sites, the turn motif and the hydrophobic motif. The common dogma has been that phosphorylation of the hydrophobic motif primes S6K1 for the phosphorylation at the activation loop by phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1). Here, we show that the turn motif is, in fact, phosphorylated first, the activation loop second, and the hydrophobic motif is third. Specifically, biochemical analyses of a construct of S6K1 lacking the C-terminal autoinhibitory domain as well as full-length S6K1, reveals that S6K1 is constitutively phosphorylated at the turn motif when expressed in insect cells and becomes phosphorylated in vitro by purified PDK1 at the activation loop. Only the species phosphorylated at the activation loop by PDK1 gets phosphorylated at the hydrophobic motif by mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in vitro. These data are consistent with a previous model in which constitutive phosphorylation of the turn motif provides the key priming step in the phosphorylation of S6K1. The data provide evidence for regulation of S6K1, where hydrophobic motif phosphorylation is not required for PDK1 to phosphorylate S6K1 at the activation loop, but instead activation loop phosphorylation of S6K1 is required for mTOR to phosphorylate the hydrophobic motif of S6K1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
In vivo role of the phosphate groove of PDK1 defined by knockin mutation.J Cell Sci. 2005 Nov 1;118(Pt 21):5023-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02617. Epub 2005 Oct 11. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16219676
-
Expression, purification, and characterization of a structurally disordered and functional C-terminal autoinhibitory domain (AID) of the 70 kDa 40S ribosomal protein S6 kinase-1 (S6K1).Protein Expr Purif. 2008 Feb;57(2):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2007.09.014. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Protein Expr Purif. 2008. PMID: 17980619 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of hydrophobic motif and activation loop phosphorylation is a consequence and not the mechanism of S6 kinase 1 inhibition by rapamycin.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013 Apr-Jun;27(2):399-408. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013. PMID: 23830390
-
PDK2: the missing piece in the receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathway puzzle.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Aug;289(2):E187-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00011.2005. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 16014356 Review.
-
mTOR Regulation of AGC Kinases: New Twist to an Old Tail.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;101(4):213-218. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000310. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34155089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein kinase B and extracellular signal-regulated kinase contribute to the chondroprotective effect of morroniside on osteoarthritis chondrocytes.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Aug;19(8):1877-86. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12559. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25754021 Free PMC article.
-
Cotranslational cis-phosphorylation of the COOH-terminal tail is a key priming step in the maturation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 15;109(20):E1221-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202741109. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22493239 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of muscle protein synthesis and the effects of catabolic states.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2147-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.039. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23769967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-expression of the RPS6KB1 and PDPK1 genes for production of activated p70S6K1 using bac-to-bac baculovirus expression system.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 17;52(1):130. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10136-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39821712 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian TOR signaling to the AGC kinases.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Dec;46(6):527-47. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2011.618113. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21981278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montagne J., Stewart M. J., Stocker H., Hafen E., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. (1999) Science 285, 2126–2129 - PubMed
-
- Martin K. A., Blenis J. (2002) Adv. Cancer Res. 86, 1–39 - PubMed
-
- Hanks S. K., Hunter T. (1995) FASEB J. 9, 576–596 - PubMed
-
- Keranen L. M., Dutil E. M., Newton A. C. (1995) Curr. Biol. 5, 1394–1403 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

