Herpes simplex virus 1 pUL34 plays a critical role in cell-to-cell spread of virus in addition to its role in virus replication
- PMID: 21561917
- PMCID: PMC3126596
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00262-11
Herpes simplex virus 1 pUL34 plays a critical role in cell-to-cell spread of virus in addition to its role in virus replication
Abstract
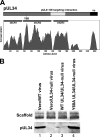
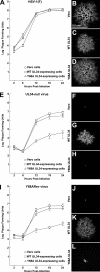
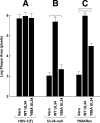
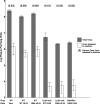
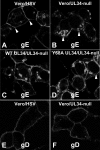
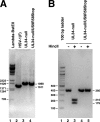
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) pUL34 plays a critical role in virus replication by mediating egress of nucleocapsids from the infected cell nucleus. We have identified a mutation in pUL34 (Y68A) that produces a major defect in virus replication and impaired nuclear egress but also profoundly inhibits cell-to-cell spread and trafficking of gE. Virion release to the extracellular medium is not affected by the Y68A mutation, indicating that the mutation specifically inhibits cell-to-cell spread. We isolated extragenic suppressors of the Y68A plaque formation defect and mapped them by a combination of high-throughput Illumina sequencing and PCR-based screening. We found that suppression is highly correlated with a nonsense mutation in the US9 gene, which plays a critical role in cell-to-cell spread of HSV-1 in neurons. The US9 mutation alone is not sufficient to suppress the Y68A spread phenotype, indicating a likely role for multiple viral factors.
Figures



References
-
- Balan P., et al. 1994. An analysis of the in vitro and in vivo phenotypes of mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 lacking glycoproteins gG, gE, gI or the putative gJ. J. Gen. Virol. 75:1245–1258 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

