Chemopreventive efficacy and mechanism of licofelone in a mouse lung tumor model via aspiration
- PMID: 21562034
- PMCID: PMC3151334
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0117
Chemopreventive efficacy and mechanism of licofelone in a mouse lung tumor model via aspiration
Abstract
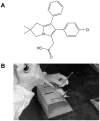
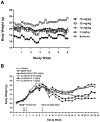
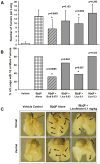
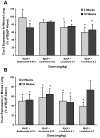
Our previous study comparing inhalation and aspiration to administer agents directly to lung indicated that aspiration route is as effective as inhalation while reducing costs for equipment and chemopreventive agent. This study evaluated the chemopreventive efficacy and mechanism of licofelone, a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-lipoxygenase (5-Lox), via oropharyngeal aspiration against mouse lung adenoma. Eight-week-old female A/J mice were given three doses of benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P; 2 mg/dose, gavage) to induce lung adenomas. After dysplasia developed, the mice were given licofelone (0, 0.03, 0.1, or 0.3 mg/kg) for 16 weeks, and tumor incidence and multiplicity in lung were measured. In addition, the expression of a series of biomarkers in lung cancer progression was evaluated at 2 and 16 weeks. Licofelone showed dose-related inhibition of B[a]P-induced tumor incidence and multiplicity at 0.03 and 0.1 mg/kg following 16-week treatment. Licofelone also showed dose-dependent inhibition of COX-2 (25%-41%) and 5-Lox (35%-61%) at 2 and 16 weeks and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA; 41%-61%) at 16 weeks. A dose-dependent increase in apoptosis (1.5- to 2.4-fold) was also observed in licofelone groups. A marginal inhibition of survivin was observed at one dose. In conclusion, this study showed that licofelone via aspiration showed chemopreventive efficacy against mouse lung adenoma with good correlation to early and late biomarkers of lung cancer progression. This is the first study to show that the aspiration route can be an excellent inexpensive alternative to inhalation for direct delivery of drugs to rodent lungs for efficacy testing of potential chemopreventive agents.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts in interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Decensi A, Costa A. Recent advances in cancer chemoprevention, with emphasis on breast and colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:694–709. - PubMed
-
- Goodman GE. Prevention of lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2000;33:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Khuri FR, Lippman SM. Lung cancer chemoprevention. Semin Surg Oncol. 2000;18:100–105. - PubMed
-
- Lippman SM, Spitz MR. Lung cancer chemoprevention: an integrated approach. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:74S–82S. - PubMed
-
- Lippman SM, Benner SE, Hong WK. Retinoid chemoprevention studies in upper aerodigestive tract and lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2025s–2028s. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous