Escalating intravenous methotrexate improves event-free survival in children with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children's Oncology Group
- PMID: 21562038
- PMCID: PMC3138679
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-322909
Escalating intravenous methotrexate improves event-free survival in children with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children's Oncology Group
Abstract
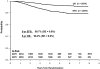
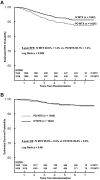
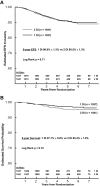
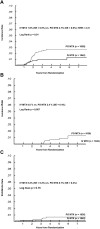
Children's Cancer Group-1991 selected 2 components from the Children's Cancer Group studies shown to be effective in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia and examined them in children with National Cancer Institute standard-risk acute B-precursor lymphoblastic leukemia. These were (1) vincristine and escalating IV methotrexate (MTX) without leucovorin rescue during the interim maintenance (IM) phases and (2) addition of a second delayed intensification (DI) phase. Eligible patients (n = 2078) were randomly assigned to regimens containing either oral (PO) MTX, PO mercaptopurine, dexamethasone, and vincristine or IV MTX during IM phases, and regimens with either single DI or double DI. Five-year event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival for patients on the PO MTX arms were 88.7% ± 1.4% and 96% ± 0.9% versus 92.6% ± 1.2% and 96.5% ± 0.8% for those on the IV MTX arms (P = .009, P = .66). Five-year EFS and overall survival for patients who received single DI were 90.9% ± 1.3% and 97.1% ± 0.8% versus 90.5% ± 1.3% and 95.4% ± 3.8% for those who received double DI (P = .71, P = .12). No advantage was found for a second DI; however, replacement of PO MTX, PO mercaptopurine, vincristine, and dexamethasone during IM with vincristine and escalating IV MTX improved EFS.
Figures
References
-
- Riehm H, Langermann HJ, Gadner H, Odenwald E, Henze G. The Berlin Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Therapy Study, 1970-1976. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1980;2(4):299–306.
-
- Henze G, Fengler R, Reiter A, Ritter J, Riehm H. Impact of early intensive reinduction therapy on event-free survival in children with low-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1990;33:483–488. - PubMed
-
- Tubergen D, Gilchrist G, O'Brien A, et al. Improved outcome with delayed intensification for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and intermediate presenting features. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11(3):527–537. - PubMed
-
- Mastrangelo R, Poplack D, Bleyer A, Riccardi R, Sather H, D'Angio G. Report and recommendations of the Rome workshop concerning poor-prognosis acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children: biologic bases for staging, stratification, and treatment. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1986;14(3):191–194. - PubMed
-
- Smith M, Arthur D, Camitta B, et al. Uniform approach to risk classification and treatment assignment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [see comments]. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(1):18–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

