Transcriptional activation of histone H4 by C/EBPβ during the mitotic clonal expansion of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation
- PMID: 21562223
- PMCID: PMC3128520
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-11-0912
Transcriptional activation of histone H4 by C/EBPβ during the mitotic clonal expansion of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation
Abstract
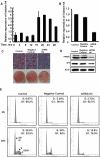
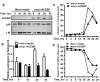
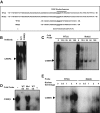
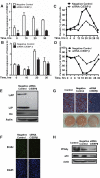
CCAAT enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) is required for both mitotic clonal expansion (MCE) and terminal differentiation during the 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation program. Whereas the mechanism of C/EBPβ during terminal differentiation is well understood, the mechanism of C/EBPβ in MCE is not. We provide evidence that histone H4, the most conserved cell cycle-related histone, the change of which is strictly correlated with DNA content change during the cell cycle, is transcriptionally activated by C/EBPβ during MCE. Expression of histone H4 is increased at 16 h after induction when 3T3-L1 preadipocytes synchronously reenter S phase, which is correlated with the sequential phosphorylation and activation of C/EBPβ, and expression was partially suppressed when A-C/EBP (dominant negative for C/EBP protein) was overexpressed. One C/EBP-binding site was identified in one of the histone H4 gene promoters (hist4h4), confirmed by both electrophoretic mobility shift assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. C/EBP-binding sites were also found in 9 of 11 other histone H4 promoters, which can also be transactivated by C/EBPβ. Knockdown of C/EBPβ by stealth small interfering RNA partially decreased H4 gene expression and arrested cells in G1 phase as indicated by bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of DNA content. This study provides new insights into why C/EBPβ is required for MCE during 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation and why C/EBPβ plays important roles in the proliferation of other cell types.
Figures
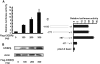
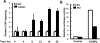


References
-
- Aziz F, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS. HiNF-D (CDP-cut/CDC2/cyclin A/pRB-complex) influences the timing of IRF-2-dependent cell cycle activation of human histone H4 gene transcription at the G1/S phase transition. J Cell Physiol. 1998a;177:453–464. - PubMed
-
- Aziz F, van Wijnen AJ, Vaughan PS, Wu SJ, Shakoori AR, Lian JB, Soprano KJ, Stein JL, Stein GS. The integrated activities of IRF-2 (HiNF-M), CDP/cut (HiNF-D) and H4TF-2 (HiNF-P) regulate transcription of a cell cycle controlled human histone H4 gene: mechanistic differences between distinct H4 genes. Mol Biol Rep. 1998b;25:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum MJ, et al. Functional role for Sp1 in the transcriptional amplification of a cell cycle regulated histone H4 gene. Biochemistry. 1995;34:7648–7658. - PubMed
-
- Borun TW, Pearson D, Paik WK. Studies of histone methylation during HELA S-3 cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1972;247:4288. - PubMed
-
- Buck M, Poli V, Van Der Geer P, Chojkier M, Hunter T. Phosphorylation of rat serine 105 or mouse threonine 217 in C/EBP beta is required for hepatocyte proliferation induced by TGF alpha. Mol Cell. 1999;4:1087–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

