Vimentin intermediate filaments modulate the motility of mitochondria
- PMID: 21562225
- PMCID: PMC3128530
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-09-0766
Vimentin intermediate filaments modulate the motility of mitochondria
Abstract
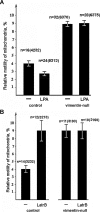
Interactions with vimentin intermediate filaments (VimIFs) affect the motility, distribution, and anchorage of mitochondria. In cells lacking VimIFs or in which VimIF organization is disrupted, the motility of mitochondria is increased relative to control cells that express normal VimIF networks. Expression of wild-type VimIF in vimentin-null cells causes mitochondrial motility to return to normal (slower) rates. In contrast, expressing vimentin with mutations in the mid-region of the N-terminal non-α-helical domain (deletions of residues 41-96 or 45-70, or substitution of Pro-57 with Arg) did not inhibit mitochondrial motility even though these mutants retain their ability to assemble into VimIFs in vivo. It was also found that a vimentin peptide consisting of residues 41-94 localizes to mitochondria. Taken together, these data suggest that VimIFs bind directly or indirectly to mitochondria and anchor them within the cytoplasm.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Deletion mutagenesis of the amino-terminal head domain of vimentin reveals dispensability of large internal regions for intermediate filament assembly and stability.Exp Cell Res. 2002 Oct 1;279(2):344-53. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5618. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12243759
-
Stability and association with the cytomatrix of mitochondrial DNA in spontaneously immortalized mouse embryo fibroblasts containing or lacking the intermediate filament protein vimentin.DNA Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;24(11):710-35. doi: 10.1089/dna.2005.24.710. DNA Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16274293
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential is regulated by vimentin intermediate filaments.FASEB J. 2015 Mar;29(3):820-7. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-259903. Epub 2014 Nov 17. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25404709 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of calmodulin, actin, and vimentin in steroid synthesis by adrenal cells.Steroids. 1997 Jan;62(1):185-9. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(96)00179-1. Steroids. 1997. PMID: 9029735 Review.
-
Roles of vimentin in health and disease.Genes Dev. 2022 Apr 1;36(7-8):391-407. doi: 10.1101/gad.349358.122. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 35487686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan-positive Recycling Endosomes Isolated from Glioma Cells.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2016 11-12;13(6):443-452. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20007. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27807067 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biomechanical basis of mitochondrial movement in eukaryotic cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4033-42. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S52132. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 24187495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dynamics: Working with the Cytoskeleton and Intracellular Organelles to Mediate Mechanotransduction.Aging Dis. 2023 Oct 1;14(5):1511-1532. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0201. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37196113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desmin Interacts Directly with Mitochondria.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8122. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218122. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143195 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical organization of vimentin intermediate filaments in living cells revealed by MoNaLISA nanoscopy.Biosci Rep. 2025 Feb 12;45(2):BSR20241133. doi: 10.1042/BSR20241133. Biosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39936518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen R, Egan B, Gabriel K, Beilharz T, Lithgow T. A conserved proline residue is present in the transmembrane-spanning domain of Tom7 and other tail-anchored protein subunits of the TOM translocase. FEBS Lett. 2002;514:347–350. - PubMed
-
- Avsyuk AY, Khodyakov AL, Baibikova EM, Solovyanova OB, Nadezhdina ES. Stability of vimentin intermediate filaments in interphasic cells. Dokl Rus Acad Nauk. 1997;357:130–133. - PubMed
-
- Baloh RH. Mitochondrial dynamics and peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscientist. 2008;14:12–18. - PubMed
-
- Brownlees J, Ackerley S, Grierson AJ, Jacobsen NJ, Shea K, Anderton BH, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, Miller CC. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease neurofilament mutations disrupt neurofilament assembly and axonal transport. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:2837–2844. - PubMed
-
- Capetanaki Y. Desmin cytoskeleton: a potential regulator of muscle mitochondrial behavior and function. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2002;12:339–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

