Apoptosis and acute kidney injury
- PMID: 21562469
- PMCID: PMC4625984
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.120
Apoptosis and acute kidney injury
Abstract
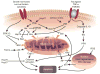
Improved mechanistic understanding of renal cell death in acute kidney injury (AKI) has generated new therapeutic targets. Clearly, the classic lesion of acute tubular necrosis is not adequate to describe the consequences of renal ischemia, nephrotoxin exposure, or sepsis on glomerular filtration rate. Experimental evidence supports a pathogenic role for apoptosis in AKI. Interestingly, proximal tubule epithelial cells are highly susceptible to apoptosis, and injury at this site contributes to organ failure. During apoptosis, well-orchestrated events converge at the mitochondrion, the organelle that integrates life and death signals generated by the BCL2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) protein family. Death requires the 'perfect storm' for outer mitochondrial membrane injury to release its cellular 'executioners'. The complexity of this process affords new targets for effective interventions, both before and after renal insults. Inhibiting apoptosis appears to be critical, because circulating factors released by the injured kidney induce apoptosis and inflammation in distant organs including the heart, lung, liver, and brain, potentially contributing to the high morbidity and mortality associated with AKI. Manipulation of known stress kinases upstream of mitochondrial injury, induction of endogenous, anti-apoptotic proteins, and improved understanding of the timing and consequences of renal cell apoptosis will inevitably improve the outcome of human AKI.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
The apoptotic program promotes tissue remodeling and fibrosis.Kidney Int. 2011 Nov;80(10):1108; author reply 1108. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.307. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 22042034 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bonventre JV, Weinberg JM. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2199–2210. - PubMed
-
- Ueda N, Kaushal GP, Shah SV. Apoptotic mechanisms in acute renal failure. Am J Med. 2000;108:403–415. - PubMed
-
- Basnakian AG, Kaushal GP, Shah SV. Apoptotic pathways of oxidative damage to renal tubular epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002;4:915–924. - PubMed
-
- Bonegio R, Lieberthal W. Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002;11:301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

