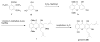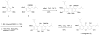Structural Characterization, Biological Effects, and Synthetic Studies on Xanthones from Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana), a Popular Botanical Dietary Supplement
- PMID: 21562610
- PMCID: PMC3090081
- DOI: 10.2174/157019308786242223
Structural Characterization, Biological Effects, and Synthetic Studies on Xanthones from Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana), a Popular Botanical Dietary Supplement
Abstract
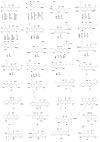
Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L., Clusiaceae) is a popular botanical dietary supplement in the United States, where it is used principally as an antioxidant. It is referred to as the "queen of fruits" in Thailand, a country of origin. The major secondary metabolites of mangosteen, the xanthones, exhibit a variety of biological activities including antibacterial, antifungal, antiinflammatory, antioxidant, antiplasmodial, cytotoxic, and potential cancer chemopreventive activities. Moreover, some of the xanthones from mangosteen have been found to influence specific enzyme activities, such as aromatase, HIV-1 protease, inhibitor κB kinase, quinone reductase, sphingomyelinase, topoisomerase and several protein kinases, and they also modulate histamine H(1) and 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor binding. Several synthetic procedures for active xanthones and their analogs have been conducted to obtain a better insight into structure-activity relationships for this compound class. This short review deals with progress made in the structural characterization of the chemical constituents of mangosteen, as well as the biological activity of pure constituents of this species and synthetic methods for the mangosteen xanthones.
Figures
References
-
- Farnsworth NR, Bunyapraphatsara N. Thai Medicinal Plants Recommended for Primary Health Care System. Medicinal Plant Information Center; Bangkok: 1992. pp. 160–162.
-
- Moongkarndi P, Kosem N, Kaslungka S, Luanratana O, Pongpan N, Neungton N. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;90:161. - PubMed
-
- Garrity AR, Morton GA, Morton JC. Nutraceutical mangosteen composition. 6730333 B1 20040504. US Patent. 2004:7.
-
- Nutrition Business Journal. NBJ’s Supplement Business Report 2007: an analysis of markets, trends, competition and strategy in the US dietary supplement industry. Penton Media Inc; San Diego: 2007. pp. 82–240.
-
- Weecharangsan W, Opanasopit P, Sukma M, Ngawhirunpat T, Sotanaphun U, Siripong P. Med Princ Pract. 2006;15:281. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources