Secretins: dynamic channels for protein transport across membranes
- PMID: 21565514
- PMCID: PMC3155655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.04.002
Secretins: dynamic channels for protein transport across membranes
Abstract
Secretins form megadalton bacterial-membrane channels in at least four sophisticated multiprotein systems that are crucial for translocation of proteins and assembled fibers across the outer membrane of many species of bacteria. Secretin subunits contain multiple domains, which interact with numerous other proteins, including pilotins, secretion-system partner proteins, and exoproteins. Our understanding of the structure of secretins is rapidly progressing, and it is now recognized that features common to all secretins include a cylindrical arrangement of 12-15 subunits, a large periplasmic vestibule with a wide opening at one end and a periplasmic gate at the other. Secretins might also play a key role in the biogenesis of their cognate secretion systems.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


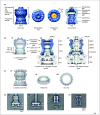

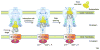
Similar articles
-
Assembly and targeting of secretins in the bacterial outer membrane.Int J Med Microbiol. 2019 Nov;309(7):151322. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Int J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31262642 Review.
-
Structural lessons on bacterial secretins.Biochimie. 2023 Feb;205:110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2022.08.019. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Biochimie. 2023. PMID: 36096236 Review.
-
Bacterial secretins: Mechanisms of assembly and membrane targeting.Protein Sci. 2020 Apr;29(4):893-904. doi: 10.1002/pro.3835. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 32020694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scaffolding Protein GspB/OutB Facilitates Assembly of the Dickeya dadantii Type 2 Secretion System by Anchoring the Outer Membrane Secretin Pore to the Inner Membrane and to the Peptidoglycan Cell Wall.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0025322. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00253-22. Epub 2022 May 12. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35546537 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the roles of pilotins and accessory proteins in secretin escort services.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012 Mar;328(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02464.x. Epub 2011 Dec 8. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22098485 Review.
Cited by
-
Commentary: The absence of protein Y4yS affects negatively the abundance of T3SS Mesorhizobium loti secretin, RhcC2, in bacterial membranes.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jul 14;6:710. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00710. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26236295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
On the path to uncover the bacterial type II secretion system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Apr 19;367(1592):1059-72. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0204. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22411978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein export according to schedule: architecture, assembly, and regulation of type III secretion systems from plant- and animal-pathogenic bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):262-310. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05017-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22688814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM of the injectisome and type III secretion systems.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Aug;75:102403. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102403. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35724552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Extended Cyclic Di-GMP Network in the Predatory Bacterium Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.J Bacteriol. 2015 Aug 31;198(1):127-37. doi: 10.1128/JB.00422-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26324450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wooldridge K. Bacterial secreted proteins: secretory mechanisms and role in pathogenesis. Caister Academic Press; 2009.
-
- Johnson TL, et al. Type II secretion: from structure to function. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;255:175–186. - PubMed
-
- Pelicic V. Type IV pili: e pluribus unum? Mol Microbiol. 2008;68:827–837. - PubMed
-
- Kirn TJ, et al. Secretion of a soluble colonization factor by the TCP type 4 pilus biogenesis pathway in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 2003;49:81–92. - PubMed
-
- Hager AJ, et al. Type IV pili-mediated secretion modulates Francisella virulence. Mol Microbiol. 2006;62:227–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

