Paused RNA polymerase II as a developmental checkpoint
- PMID: 21565610
- PMCID: PMC4257488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.021
Paused RNA polymerase II as a developmental checkpoint
Abstract
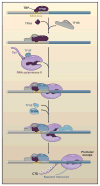
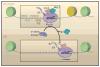
The textbook view of gene activation is that the rate-limiting step is the interaction of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) with the gene's promoter. However, studies in a variety of systems, including human embryonic stem cells and the early Drosophila embryo, have begun to challenge this view. There is increasing evidence that differential gene expression often depends on the regulation of transcription elongation via the release of Pol II from the proximal promoter. I review the implications of this mechanism of gene activation with respect to the orderly unfolding of complex gene networks governing animal development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arndt KM, Kane CM. Running with RNA polymerase: eukaryotic transcript elongation. Trends Genet. 2003;19:543–550. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986;321:702–706. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

