A hormone-dependent module regulating energy balance
- PMID: 21565616
- PMCID: PMC3129781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.013
A hormone-dependent module regulating energy balance
Abstract
Under fasting conditions, metazoans maintain energy balance by shifting from glucose to fat burning. In the fasted state, SIRT1 promotes catabolic gene expression by deacetylating the forkhead factor FOXO in response to stress and nutrient deprivation. The mechanisms by which hormonal signals regulate FOXO deacetylation remain unclear, however. We identified a hormone-dependent module, consisting of the Ser/Thr kinase SIK3 and the class IIa deacetylase HDAC4, which regulates FOXO activity in Drosophila. During feeding, HDAC4 is phosphorylated and sequestered in the cytoplasm by SIK3, whose activity is upregulated in response to insulin. SIK3 is inactivated during fasting, leading to the dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of HDAC4 and to FOXO deacetylation. SIK3 mutant flies are starvation sensitive, reflecting FOXO-dependent increases in lipolysis that deplete triglyceride stores; reducing HDAC4 expression restored lipid accumulation. Our results reveal a hormone-regulated pathway that functions in parallel with the nutrient-sensing SIRT1 pathway to maintain energy balance.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

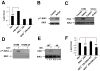


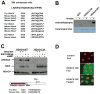


Comment in
-
Metabolic homeostasis: HDACs take center stage.Cell. 2011 May 13;145(4):497-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.017. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21565608 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic disease: New role for HDACs in glucose homeostasis.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Jul 1;10(7):492. doi: 10.1038/nrd3483. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21720402 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D, Unterman TG. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Signaling pathways in skeletal muscle remodeling. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:19–37. - PubMed
-
- Berdeaux R, Goebel N, Banaszynski L, Takemori H, Wandless T, Shelton GD, Montminy M. SIK1 is a class II HDAC kinase that promotes survival of skeletal myocytes. Nat Med. 2007;13:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Bohni R, Riesgo-Escovar J, Oldham S, Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Andruss BF, Beckingham K, Hafen E. Autonomous control of cell and organ size by CHICO, a Drosophila homolog of vertebrate IRS1-4. Cell. 1999;97:865–875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK077979/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084947/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM084947/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM040613/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK049777/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK077979/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077979/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS056316/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS031249/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040963/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049777/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

