Halogenated phenolic contaminants inhibit the in vitro activity of the thyroid-regulating deiodinases in human liver
- PMID: 21565810
- PMCID: PMC3216408
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr117
Halogenated phenolic contaminants inhibit the in vitro activity of the thyroid-regulating deiodinases in human liver
Abstract
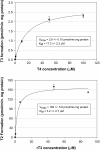
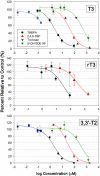
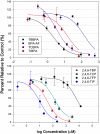
Halogenated contaminants, particularly brominated flame retardants, disrupt circulating levels of thyroid hormones (THs), potentially affecting growth and development. Disruption may be mediated by impacts on deiodinase (DI) activity, which regulate the levels of active hormones available to bind to nuclear receptors. The goal of this study was to develop a mass spectrometry-based method for measuring the activity of DIs in human liver microsomes and to examine the effect of halogenated phenolic contaminants on DI activity. Thyroxine (T4) and reverse triiodothyronine (rT3) deiodination kinetics were measured by incubating pooled human liver microsomes with T4 or rT3 and monitoring the production of T3, rT3, 3,3'-diiodothyronine, and 3-monoiodothyronine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Using this method, we examined the effects of several halogenated contaminants, including 2,2',4,4',5-pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 99), several hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers (OH-BDEs), tribromophenol, tetrabromobisphenol A, and triclosan, on DI activity. The Michaelis constants (K(M)) of rT3 and T4 deiodination were determined to be 3.2 ± 0.7 and 17.3 ± 2.3μM. The V(max) was 160 ± 5.8 and 2.8 ± 0.10 pmol/min.mg protein, respectively. All studied contaminants inhibited DI activity in a dose-response manner, with the exception of BDE 99 and two OH-BDEs. 5'-Hydroxy 2,2',4,4',5-pentabromodiphenyl ether was found to be the most potent inhibitor of DI activity, and phenolic structures containing iodine were generally more potent inhibitors of DI activity relative to brominated, chlorinated, and fluorinated analogues. This study suggests that some halogenated phenolics, including current use compounds such as plastic monomers, flame retardants, and their metabolites, may disrupt TH homeostasis through the inhibition of DI activity in vivo.
Figures
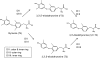
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of thyroid hormone sulfotransferase activity by brominated flame retardants and halogenated phenolics.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Nov 18;26(11):1692-702. doi: 10.1021/tx400342k. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24089703 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential deiodination of thyroxine in human thyroid gland.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):890-6. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-890. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982. PMID: 6896880
-
In vitro metabolism of BDE-47, BDE-99, and α-, β-, γ-HBCD isomers by chicken liver microsomes.Environ Res. 2015 Nov;143(Pt A):221-8. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Oct 24. Environ Res. 2015. PMID: 26505652
-
A Halogen Bonding Perspective on Iodothyronine Deiodinase Activity.Molecules. 2020 Mar 14;25(6):1328. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061328. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32183289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their hydroxylated/methoxylated analogs: environmental sources, metabolic relationships, and relative toxicities.Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;63(5-12):179-88. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.008. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011. PMID: 21439595 Review.
Cited by
-
Biotransformation of 2,4,6-tris(2,4,6-tribromophenoxy)-1,3,5-triazine (TTBP-TAZ) can contribute to high levels of 2,4,6-tribromophenol (2,4,6-TBP) in humans.Environ Int. 2022 Jan;158:106943. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106943. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Environ Int. 2022. PMID: 34717176 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Prenatal Exposure to Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) and Infant Birth Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis and an Experimental Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Mar 7;14(3):268. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030268. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28272363 Free PMC article.
-
Screening the ToxCast Phase 1, Phase 2, and e1k Chemical Libraries for Inhibitors of Iodothyronine Deiodinases.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Apr 1;168(2):430-442. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy302. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30561685 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between brominated flame retardants in house dust and hormone levels in men.Sci Total Environ. 2013 Feb 15;445-446:177-84. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.017. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Sci Total Environ. 2013. PMID: 23333513 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of thyroid hormone sulfotransferase activity by brominated flame retardants and halogenated phenolics.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Nov 18;26(11):1692-702. doi: 10.1021/tx400342k. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24089703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auf'mkolk M, Koehrle J, Hesch R-D, Cody V. Inhibition of rat liver iodothyronine deiodinase: Interaction of aurones with the iodothyronine ligand-binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:11623–11630. - PubMed
-
- Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR. Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr. Rev. 2002;23:38–89. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira ACF, Lisboa PC, Oliveira KJ, Lima LP, Barros IA, Carvalho DP. Inhibition of thyroid type1 deiodinase activity by flavonoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002;40:913–917. - PubMed
-
- Galton VA. The roles of the iodothyronine deiodinases in mammalian development. Thyroid. 2005;15:823–834. - PubMed

