Rosuvastatin in diabetic hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 21566054
- PMCID: PMC3137581
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010090987
Rosuvastatin in diabetic hemodialysis patients
Abstract
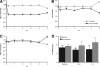
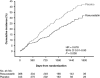
A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in diabetic patients receiving hemodialysis showed no effect of atorvastatin on a composite cardiovascular endpoint, but analysis of the component cardiac endpoints suggested that atorvastatin may significantly reduce risk. Because the AURORA (A Study to Evaluate the Use of Rosuvastatin in Subjects on Regular Hemodialysis: An Assessment of Survival and Cardiovascular Events) trial included patients with and without diabetes, we conducted a post hoc analysis to determine whether rosuvastatin might reduce the risk of cardiac events in diabetic patients receiving hemodialysis. Among the 731 participants with diabetes, traditional risk factors such as LDL-C, smoking, and BP did not associate with cardiac events (cardiac death and nonfatal myocardial infarction). At baseline, only age and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were independent risk factors for cardiac events. Assignment to rosuvastatin associated with a nonsignificant 16.2% reduction in risk for the AURORA trial's composite primary endpoint of cardiac death, nonfatal MI, or fatal or nonfatal stroke (HR 0.84; 95% CI 0.65 to 1.07). There was no difference in overall stroke, but the rosuvastatin group had more hemorrhagic strokes than the placebo group (12 versus two strokes, respectively; HR, 5.21; 95% CI 1.17 to 23.27). Rosuvastatin treatment significantly reduced the rates of cardiac events by 32% among patients with diabetes (HR 0.68; 95% CI 0.51 to 0.90). In conclusion, among hemodialysis patients with diabetes mellitus, rosuvastatin might reduce the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiac events.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures
Comment in
-
Sunrise of statins after AURORA and 4D?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Jul;22(7):1184-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050504. Epub 2011 Jun 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21680649 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemodialysis.N Engl J Med. 2009 Apr 2;360(14):1395-407. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810177. Epub 2009 Mar 30. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19332456 Clinical Trial.
-
Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein.N Engl J Med. 2008 Nov 20;359(21):2195-207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807646. Epub 2008 Nov 9. N Engl J Med. 2008. PMID: 18997196 Clinical Trial.
-
Rosuvastatin in hemodialysis: short-term effects on lipids and C-reactive protein.J Nephrol. 2009 Jan-Feb;22(1):83-9. J Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19229822 Clinical Trial.
-
The Jupiter study, CRP screening, and aggressive statin therapy-implications for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Aug;3(4):309-15. doi: 10.1177/1753944709337056. Epub 2009 May 21. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2009. PMID: 19460829 Review.
-
Rosuvastatin: a review of its use in the prevention of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy women or men with normal LDL-C levels and elevated hsCRP levels.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10(6):383-400. doi: 10.2165/11204600-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21090831 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid abnormalities in kidney disease and management strategies.World J Nephrol. 2015 Feb 6;4(1):83-91. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i1.83. World J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25664249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statin therapy associated mortality in hyperlipidemic dialysis patients with percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction, a retrospective cohort study.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 29;10(21):e39906. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39906. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39553683 Free PMC article.
-
Statins in the management of dyslipidemia associated with chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Feb 21;8(4):214-23. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.33. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22349484 Review.
-
Pharmacological and non pharmacological strategies in the management of coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2015;11(3):261-9. doi: 10.2174/1573403x1103150514155757. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25981315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lipid story in chronic kidney disease: a long story with a happy end?Int Urol Nephrol. 2013 Oct;45(5):1273-87. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0296-8. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23054316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists' (CTT) Collaborators, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Collins R, Keech A, Simes J, Peto R, Armitage J, Baigent C: Efficacy of cholesterol-lowering therapy in 18,686 people with diabetes in 14 randomised trials of statins: a meta-analysis. Lancet 371: 117–125, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Shepherd J, Kastelein JP, Bittner VA, Carmena R, Deedwania PC, Breazna A, Dobson S, Wilson DJ, Zuckerman AL, Wenger NK: Treating to New Targets Steering Committee and Investigators: Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with coronary artery disease, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease. Mayo Clin Proc 83: 870–879, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Keech A, Shepherd J, Sacks F, Tonkin A, Packard C, Pfeffer M, Simes J, Isles C, Furberg C, West M, Craven T, Curhan G: Effect of pravastatin in people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 3748–3754, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Mason NA, Bailie GR, Satayathum S, Bragg-Gresham JL, Akiba T, Akizawa T, Combe C, Rayner HC, Saito A, Gillespie BW, Young EW: HMG-coenzyme a reductase inhibitor use is associated with mortality reduction in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 45: 119–126, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Seliger SL, Weiss NS, Gillen DL, Kestenbaum B, Ball A, Sherrard DJ, Stehman-Breen CO: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are associated with reduced mortality in ESRD patients. Kidney Int 61: 297–304, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

