An (1)O2 route to γ-hydroxyalkenal phospholipids by vitamin E-induced fragmentation of hydroperoxydiene-derived endoperoxides
- PMID: 21568309
- PMCID: PMC3141739
- DOI: 10.1021/tx200093m
An (1)O2 route to γ-hydroxyalkenal phospholipids by vitamin E-induced fragmentation of hydroperoxydiene-derived endoperoxides
Abstract
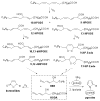
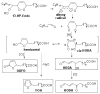
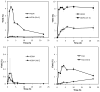
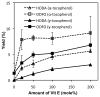
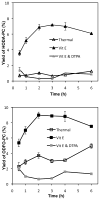
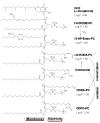
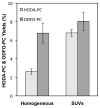
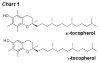
Biologically active phospholipids that incorporate an oxidatively truncated acyl chain terminated by a γ-hydroxyalkenal are generated in vivo. The γ-hydroxyalkenal moiety protrudes from lipid bilayers like whiskers that serve as ligands for the scavenger receptor CD36, fostering endocytosis, e.g., of oxidatively damaged photoreceptor cell outer segments by retinal pigmented endothelial cells. They also covalently modify proteins generating carboxyalkyl pyrroles incorporating the ε-amino group of protein lysyl residues. We postulated that γ-hydroxyalkenals could be generated, e.g., in the eye, through fragmentation of hydroperoxy endoperoxides produced in the retina through reactions of singlet molecular oxygen with polyunsaturated phospholipids. Since phospholipid esters are far more abundant in the retina than free fatty acids, we examined the influence of a membrane environment on the fate of hydroperoxy endoperoxides. We now report that linoleate hydroperoxy endoperoxides in thin films and their phospholipid esters in biomimetic membranes fragment to γ-hydroxyalkenals, and fragmentation is stoichiometrically induced by vitamin E. The product distribution from fragmentation of the free acid in the homogeneous environment of a thin film is remarkably different from that from the corresponding phospholipid in a membrane. In the membrane, further oxidation of the initially formed γ-hydroxyalkenal to a butenolide is disfavored. A conformational preference for the γ-hydroxyalkenal, to protrude from the membrane into the aqueous phase, may protect it from oxidation induced by lipid hydroperoxides that remain buried in the lipophilic membrane core.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures

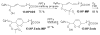
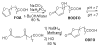




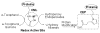
Similar articles
-
Gamma-hydroxyalkenals are oxidatively cleaved through Michael addition of acylperoxy radicals and fragmentation of intermediate beta-hydroxyperesters.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Sep 22;126(37):11522-8. doi: 10.1021/ja048060i. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15366898
-
Polyunsaturated phospholipids promote the oxidation and fragmentation of gamma-hydroxyalkenals: formation and reactions of oxidatively truncated ether phospholipids.J Lipid Res. 2008 Apr;49(4):832-46. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700598-JLR200. Epub 2007 Dec 29. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18165704 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative fragmentation of hydroxy octadecadienoates generates biologically active gamma-hydroxyalkenals.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 May 12;126(18):5699-708. doi: 10.1021/ja038756w. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15125662
-
Lipid hydroperoxides as a source of singlet molecular oxygen.Subcell Biochem. 2014;77:3-20. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7920-4_1. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24374914 Review.
-
Vitamin E and its function in membranes.Prog Lipid Res. 1999 Jul;38(4):309-36. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(99)00008-9. Prog Lipid Res. 1999. PMID: 10793887 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolevuglandins as mediators of disease and the development of dicarbonyl scavengers as pharmaceutical interventions.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Jan;205:107418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107418. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31629006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Critical Paraoxonase 1 Residues Involved in High Density Lipoprotein Interaction.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1890-1904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.678334. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26567339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg ME, Li XM, Gugiu BG, Gu X, Qin J, Salomon RG, Hazen SL. The lipid whisker model of the structure of oxidized cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:2385–2396. - PubMed
-
- Sun M, Finnemann SC, Febbraio M, Shan L, Annangudi SP, Podrez EA, Hoppe G, Darrow R, Organisciak DT, Salomon RG, Silverstein RL, Hazen SL. Light-induced oxidation of photoreceptor outer segment phospholipids generates ligands for CD36-mediated phagocytosis by retinal pigment epithelium: a potential mechanism for modulating outer segment phagocytosis under oxidant stress conditions. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:4222–4230. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu X, Sun M, Gugiu B, Hazen S, Crabb JW, Salomon RG. Oxidatively truncated docosahexaenoate phospholipids: total synthesis, generation, and peptide adduction chemistry. J Org Chem. 2003;68:3749–3761. - PubMed
-
- Kaur K, Salomon RG, O’Neil J, Hoff HF. (Carboxyalkyl)pyrroles in human plasma and oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997;10:1387–1396. - PubMed
-
- Gu X, Meer SG, Miyagi M, Rayborn ME, Hollyfield JG, Crabb JW, Salomon RG. Carboxyethylpyrrole protein adducts and autoantibodies, biomarkers for age-related macular degeneration. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:42027–42035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

