Mapping fetal brain development in utero using magnetic resonance imaging: the Big Bang of brain mapping
- PMID: 21568716
- PMCID: PMC3682118
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071910-124654
Mapping fetal brain development in utero using magnetic resonance imaging: the Big Bang of brain mapping
Abstract
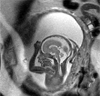
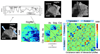
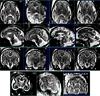
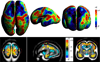
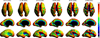
The development of tools to construct and investigate probabilistic maps of the adult human brain from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has led to advances in both basic neuroscience and clinical diagnosis. These tools are increasingly being applied to brain development in adolescence and childhood, and even to neonatal and premature neonatal imaging. Even earlier in development, parallel advances in clinical fetal MRI have led to its growing use as a tool in challenging medical conditions. This has motivated new engineering developments encompassing optimal fast MRI scans and techniques derived from computer vision, the combination of which allows full 3D imaging of the moving fetal brain in utero without sedation. These promise to provide a new and unprecedented window into early human brain growth. This article reviews the developments that have led us to this point, examines the current state of the art in the fields of fast fetal imaging and motion correction, and describes the tools to analyze dynamically changing fetal brain structure. New methods to deal with developmental tissue segmentation and the construction of spatiotemporal atlases are examined, together with techniques to map fetal brain growth patterns.
Figures

References
-
- Toga Arthur W, Thompson Paul M. Temporal dynamics of brain anatomy. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2003;5:119–145. - PubMed
-
- Mazziotta JC, Toga AW, Evans AC, Fox P, Lancaster J. A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. NeuroImage. 1995;2:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Miller Michael I, Trouve Alain, Younes Laurent. On the metrics and euler-lagrange equations of computational anatomy. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2002;4:375–405. - PubMed
-
- Thompson Paul M, Mega1 Michael S, Woods Roger P, Zoumalan Chris I, Lindshield Chris J, Blanton Rebecca E, Moussai Jacob, Holmes Colin J, Cummings Jeffrey L, Toga Arthur W. Cortical change in alzheimer’s disease detected with a disease-specific population-based brain atlas. Cereb. Cortex. 2001;11(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Lerch JP, Pruessner JC, Zijdenbos A, Hampel H, Teipel SJ, Evans AC. Focal decline of cortical thickness in alzheimers disease identified by computational neuroanatomy. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:995–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

