Post-prandial reactive hypoglycaemia and diarrhea caused by idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying: a case report
- PMID: 21569503
- PMCID: PMC3113993
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-177
Post-prandial reactive hypoglycaemia and diarrhea caused by idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying: a case report
Abstract
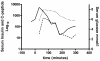
Introduction: The majority of cases of post-prandial reactive hypoglycemia are considered idiopathic. Abnormalities of B-cell function and glucose regulation by insulin and glucagon have been postulated as causes but associated gastrointestinal dysfunction has not been reported. We report the first case of accelerated gastric emptying associated with post-prandial reactive hypoglycemia, abdominal bloating and diarrhea. We consider that gastric dysmotility is an important cause of this condition as treatment of the underlying abnormal gastric emptying allows effective control of symptoms.
Case presentation: A 20-year-old Caucasian woman presented with post-prandial fatigue, sweating, nausea, faintness and intermittent confusion, which had led to pre-syncope and syncope on occasions. She also experienced marked abdominal bloating and diarrhea over the same period. These episodes responded to oral administration of sweet drinks. Her symptoms were ameliorated by modification of her diet.
Conclusion: This is an original case report of the association of idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying with post-prandial reactive hypoglycemia and diarrhea. Family physicians, endocrinologists and gastroenterologists often consult patients with a constellation of post-prandial symptoms, which are considered to be idiopathic in most cases. This case indicates that gastric dysmotility might be the primary cause of these symptoms in some patients and, if found, offers a therapeutic target which in our case was successful.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying presenting in adults with post-prandial diarrhea and reactive hypoglycemia: a case series.J Med Case Rep. 2012 May 19;6:132. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-132. J Med Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 22607835 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics associated with idiopathic rapid gastric emptying in patients referred for gastric emptying studies.J Dig Dis. 2021 Jun;22(6):329-333. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12990. Epub 2021 May 11. J Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 33840163
-
Gastric electrical stimulation: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(16):1-79. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074486 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives on the management of gastroparesis.J Postgrad Med. 2005 Jan-Mar;51(1):54-60. J Postgrad Med. 2005. PMID: 15793344 Review.
-
Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment.Diabet Med. 2002 Mar;19(3):177-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00658.x. Diabet Med. 2002. PMID: 11918620 Review.
Cited by
-
Idiopathic accelerated gastric emptying presenting in adults with post-prandial diarrhea and reactive hypoglycemia: a case series.J Med Case Rep. 2012 May 19;6:132. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-132. J Med Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 22607835 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycemia Associated With Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.JCEM Case Rep. 2024 Nov 4;2(11):luae205. doi: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae205. eCollection 2024 Nov. JCEM Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39498469 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the alpha glucosidase inhibitor acarbose in patients with 'Middleton syndrome': normal gastric anatomy but with accelerated gastric emptying causing postprandial reactive hypoglycemia and diarrhea.Can J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul;27(7):403-4. doi: 10.1155/2013/791803. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23862171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonetti F, Morviducci L, Giaccari A, Sbraccia P, Caiola S, Zorretta D, Lostia O, Tamburrano G. Idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia: a role for glucagon? J Endocrinol Invest. 1992;15(4):273–278. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

