A hidden two-locus disease association pattern in genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 21569557
- PMCID: PMC3116488
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-156
A hidden two-locus disease association pattern in genome-wide association studies
Abstract
Background: Recent association analyses in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) mainly focus on single-locus association tests (marginal tests) and two-locus interaction detections. These analysis methods have provided strong evidence of associations between genetics variances and complex diseases. However, there exists a type of association pattern, which often occurs within local regions in the genome and is unlikely to be detected by either marginal tests or interaction tests. This association pattern involves a group of correlated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The correlation among SNPs can lead to weak marginal effects and the interaction does not play a role in this association pattern. This phenomenon is due to the existence of unfaithfulness: the marginal effects of correlated SNPs do not express their significant joint effects faithfully due to the correlation cancelation.
Results: In this paper, we develop a computational method to detect this association pattern masked by unfaithfulness. We have applied our method to analyze seven data sets from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC). The analysis for each data set takes about one week to finish the examination of all pairs of SNPs. Based on the empirical result of these real data, we show that this type of association masked by unfaithfulness widely exists in GWAS.
Conclusions: These newly identified associations enrich the discoveries of GWAS, which may provide new insights both in the analysis of tagSNPs and in the experiment design of GWAS. Since these associations may be easily missed by existing analysis tools, we can only connect some of them to publicly available findings from other association studies. As independent data set is limited at this moment, we also have difficulties to replicate these findings. More biological implications need further investigation.
Availability: The software is freely available at http://bioinformatics.ust.hk/hidden_pattern_finder.zip.
Figures

 and
and  . In this figure, the marginal coefficient
. In this figure, the marginal coefficient  and
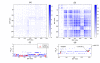
and  are shown as projections (marked with bold red color) of Y on X1 and X2, respectively. (a) X1 is not correlated with X2. (b) X1 is positively correlated with X2. (c) X1 is negatively correlated with X2. (d) X1 is positively correlated with X2 but the sign of β1 is the opposite of the sign of β2. Scenario (c) and Scenario (d) illustrate unfaithfulness.
are shown as projections (marked with bold red color) of Y on X1 and X2, respectively. (a) X1 is not correlated with X2. (b) X1 is positively correlated with X2. (c) X1 is negatively correlated with X2. (d) X1 is positively correlated with X2 but the sign of β1 is the opposite of the sign of β2. Scenario (c) and Scenario (d) illustrate unfaithfulness.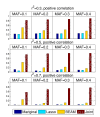


Similar articles
-
Detecting purely epistatic multi-locus interactions by an omnibus permutation test on ensembles of two-locus analyses.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Sep 17;10:294. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-294. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19761607 Free PMC article.
-
GWIS--model-free, fast and exhaustive search for epistatic interactions in case-control GWAS.BMC Genomics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S3-S10. Epub 2013 May 28. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23819779 Free PMC article.
-
Using genome-wide pathway analysis to unravel the etiology of complex diseases.Genet Epidemiol. 2009 Jul;33(5):419-31. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20395. Genet Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19235186
-
Bioinformatics challenges for genome-wide association studies.Bioinformatics. 2010 Feb 15;26(4):445-55. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp713. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20053841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Revolution in Cutaneous Biology: The Era of Genome-Wide Association Studies and Statistical, Big Data, and Computational Topics.J Invest Dermatol. 2017 May;137(5):e113-e118. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.03.047. J Invest Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28411841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chapter 10: Mining genome-wide genetic markers.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(12):e1002828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002828. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23300418 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

