Individual differences in cognition, affect, and performance: behavioral, neuroimaging, and molecular genetic approaches
- PMID: 21569853
- PMCID: PMC3482491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.04.040
Individual differences in cognition, affect, and performance: behavioral, neuroimaging, and molecular genetic approaches
Abstract
We describe the use of behavioral, neuroimaging, and genetic methods to examine individual differences in cognition and affect, guided by three criteria: (1) relevance to human performance in work and everyday settings; (2) interactions between working memory, decision-making, and affective processing; and (3) examination of individual differences. The results of behavioral, functional MRI (fMRI), event-related potential (ERP), and molecular genetic studies show that analyses at the group level often mask important findings associated with sub-groups of individuals. Dopaminergic/noradrenergic genes influencing prefrontal cortex activity contribute to inter-individual variation in working memory and decision behavior, including performance in complex simulations of military decision-making. The interactive influences of individual differences in anxiety, sensation seeking, and boredom susceptibility on evaluative decision-making can be systematically described using ERP and fMRI methods. We conclude that a multi-modal neuroergonomic approach to examining brain function (using both neuroimaging and molecular genetics) can be usefully applied to understanding individual differences in cognition and affect and has implications for human performance at work.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

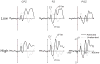

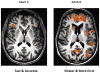
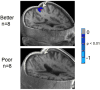
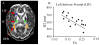
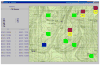
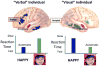

Comment in
-
Expanding horizons in ergonomics research.Neuroimage. 2012 Jan 2;59(1):149-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.060. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21816226 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ando J, Ono Y, Wright MJ. Genetic structure of spatial and verbal working memory. Behav Gen. 2001;31:615–624. - PubMed
-
- Arrabito GR, Abel SM, Lam K. Methods for mitigating the vigilance decrement in an auditory sonar monitoring task: A research synthesis. Canad Acoust. 2007;35:15–24.
-
- Avery RA, Franowicz JS, Studholme C, van Dyck CH, Arnsten AF. The alpha-2A-adrenoceptor agonist, guanfacine, increases regional cerebral blood flow in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of monkeys performing a spatial working memory task. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;23:240–249. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley A. Working memory. Science. 1992;255(5044):556–559. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JH, Scoriels L, Munafò MR. Meta-analysis of the cognitive effects of the catechol-O- methyltransferase gene Val158/108Met polymorphism. Biol Psychiat. 2008;64:137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

