Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of radiolabeled bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine) coordination complexes as cell death imaging agents
- PMID: 21570306
- PMCID: PMC3102142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.04.029
Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of radiolabeled bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine) coordination complexes as cell death imaging agents
Erratum in
- Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Sep 1;19(17):5277. Moore, Stephen K [added]
Abstract
The aim of this study was the development of (⁹⁹m)Tc labeled bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine) (Zn²⁺-DPA) coordination complexes, and the in vivo evaluation of their usefulness as radiotracers for the detection of cell death. DPA ligand 1 was labeled with (⁹⁹m)Tc via the (⁹⁹m)Tc-tricarbonyl core ([(⁹⁹m)Tc(CO)₃-1]³⁺) or via HYNIC ((⁹⁹m)Tc-HYNIC-1) in good radiochemical yields. Highest in vitro stabilities were demonstrated for [(⁹⁹m)Tc(CO)₃-1]³⁺. A mouse model of hepatic apoptosis (anti-Fas mAb) was used to demonstrate binding to apoptotic cells. (⁹⁹m)Tc-HYNIC-1 showed the best targeting of apoptotic hepatic tissue with a 2.2 times higher liver uptake in anti-Fas treated mice as compared to healthy animals. A rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury was used to further explore the ability of the (⁹⁹m)Tc-labeled Zn²⁺-DPA coordination complexes to target cell death. Selective accumulation could be detected for both tracers in the area at risk, correlating with histological proof of cell death. Area at risk to normal tissue uptake ratios were 3.82 for [(⁹⁹m)Tc(CO)₃-1]³⁺ and 5.45 for (⁹⁹m)Tc-HYNIC-1.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
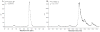
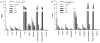

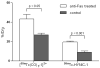
Similar articles
-
Technetium-99m HYNIC-annexin V: a potential radiopharmaceutical for the in-vivo detection of apoptosis.Eur J Nucl Med. 1999 Oct;26(10):1251-8. doi: 10.1007/s002590050580. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999. PMID: 10541822
-
Clickable, hydrophilic ligand for fac-[M(I)(CO)3](+) (M = Re/(99m)Tc) applied in an S-functionalized α-MSH peptide.Bioconjug Chem. 2014 Mar 19;25(3):579-92. doi: 10.1021/bc5000115. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Bioconjug Chem. 2014. PMID: 24568284 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Characterization, and Initial Biological Evaluation of [99m Tc]Tc-Tricarbonyl-labeled DPA-α-MSH Peptide Derivatives for Potential Melanoma Imaging.ChemMedChem. 2018 Jun 6;13(11):1146-1158. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800110. Epub 2018 Apr 23. ChemMedChem. 2018. PMID: 29659163
-
Necrosis avidity of (99m)Tc(CO)3-labeled pamoic acid derivatives: synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation in animal models of necrosis.Bioconjug Chem. 2007 Nov-Dec;18(6):1924-34. doi: 10.1021/bc700236j. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Bioconjug Chem. 2007. PMID: 17929883
-
Infection detection in mice using 99mTc-labeled HYNIC and N2S2 chelate conjugated to the antimicrobial peptide UBI 29-41.Nucl Med Biol. 2004 May;31(4):503-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2003.11.009. Nucl Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 15093821
Cited by
-
Characterization of [(99m)Tc]Duramycin as a SPECT Imaging Agent for Early Assessment of Tumor Apoptosis.Mol Imaging Biol. 2015 Dec;17(6):838-47. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0852-6. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015. PMID: 25896815 Free PMC article.
-
Library synthesis, screening, and discovery of modified Zinc(II)-Bis(dipicolylamine) probe for enhanced molecular imaging of cell death.Bioconjug Chem. 2014 Apr 16;25(4):724-37. doi: 10.1021/bc500003x. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Bioconjug Chem. 2014. PMID: 24575875 Free PMC article.
-
Avenues to molecular imaging of dying cells: Focus on cancer.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1713-1768. doi: 10.1002/med.21495. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29528513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenoxide-Bridged Zinc(II)-Bis(dipicolylamine) Probes for Molecular Imaging of Cell Death.Bioconjug Chem. 2016 Feb 17;27(2):363-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00447. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Bioconjug Chem. 2016. PMID: 26334386 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile RNA interference nanoplatform for systemic delivery of RNAs.ACS Nano. 2014 May 27;8(5):4559-70. doi: 10.1021/nn500085k. Epub 2014 May 1. ACS Nano. 2014. PMID: 24779637 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

