Hemodynamic characteristics of midazolam, propofol, and dexmedetomidine in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 21570617
- PMCID: PMC3828053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2010.09.006
Hemodynamic characteristics of midazolam, propofol, and dexmedetomidine in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Study objective: To study the effect of intravenous (IV) sedation on blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and respiratory rates (RR) to determine if IV sedatives differ with respect to their effect on BP, HR, and RR.
Design: Prospective, randomized, single-blinded, placebo-controlled study.
Setting: Monitored patient care room at a clinical research center.
Subjects: 60 healthy ASA physical status 1 volunteers.
Interventions: Subjects were randomized to receive, in increasing doses, one of three IV sedatives: propofol, midazolam, or dexmedetomidine; or saline control.
Measurements: Blood pressure (systolic, diastolic), HR, and RR were recorded.
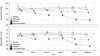
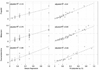
Main results: A significant dose-dependent BP reduction occurred with dexmedetomidine and, to a lesser degree, with propofol; and there was good agreement of predicted versus measured drug concentrations for all sedatives. Blood pressure and HR of participants who received midazolam did not change.
Conclusions: When administered in sedative doses, dexmedetomidine and, to a lesser extent, midazolam, reduces BP in a dose-dependent fashion. Dexmedetomidine also reduces HR. Midazolam does not affect BP or HR.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- DeFrances CJ, Lucas CA, Buie VC, Golosinskiy A. 2006 National Hospital Discharge Survey. Natl Health Stat Report. 2008;(5):1–20. - PubMed
-
- Chang C, Uchiyama A, Ma L, Mashimo T, Fujino Y. A comparison of the effects on respiratory carbon dioxide response, arterial blood pressure, and heart rate of dexmedetomidine, propofol, and midazolam in sevoflurane-anesthetized rabbits. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Heard C, Burrows F, Johnson K, Joshi P, Houck J, Lerman J. A comparison of dexmedetomidine-midazolam with propofol for maintenance of anesthesia in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Anesth Analg. 2008;107:1832–1839. - PubMed
-
- Phan H, Nahata MC. Clinical uses of dexmedetomidine in pediatric patients. Paediatr Drugs. 2008;10:49–69. - PubMed
-
- Koroglu A, Demirbilek S, Teksan H, Sagir O, But AK, Ersoy MO. Sedative, haemodynamic and respiratory effects of dexmedetomidine in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging examination: preliminary results. Br J Anaesth. 2005;94:821–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

