Silencing hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα in neonatal mice improves lung architecture via enhanced proliferation of alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 21571903
- PMCID: PMC3154632
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00082.2011
Silencing hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα in neonatal mice improves lung architecture via enhanced proliferation of alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
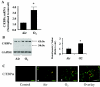
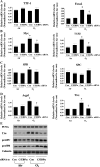
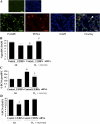
Postnatal lung development requires proliferation and differentiation of specific cell types at precise times to promote proper alveolar formation. Hyperoxic exposure can disrupt alveolarization by inhibiting cell growth; however, it is not fully understood how this is mediated. The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα) is highly expressed in the lung and plays a role in cell proliferation and differentiation in many tissues. After 72 h of hyperoxia, C/EBPα expression was significantly enhanced in the lungs of newborn mice. The increased C/EBPα protein was predominantly located in alveolar type II cells. Silencing of C/EBPα with a transpulmonary injection of C/EBPα small interfering RNA (siRNA) prior to hyperoxic exposure reduced expression of markers of type I cell and differentiation typically observed after hyperoxia but did not rescue the altered lung morphology at 72 h. Nevertheless, when C/EBPα hyperoxia-exposed siRNA-injected mice were allowed to recover for 2 wk in room air, lung epithelial cell proliferation was increased and lung morphology was restored compared with hyperoxia-exposed control siRNA-injected mice. These data suggest that C/EBPα is an important regulator of postnatal alveolar epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation during injury and repair.
Figures




References
-
- Alejandre-Alcazar MA, Kwapiszewska G, Reiss I, Amarie OV, Marsh LM, Sevilla-Perez J, Wygrecka M, Eul B, Kobrich S, Hesse M, Schermuly RT, Seeger W, Eickelberg O, Morty RE. Hyperoxia modulates TGF-β/BMP signaling in a mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L537–L549, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Basseres DS, Levantini E, Ji H, Monti S, Elf S, Dayaram T, Fenyus M, Kocher O, Golub T, Wong KK, Halmos B, Tenen DG. Respiratory failure due to differentiation arrest and expansion of alveolar cells following lung-specific loss of the transcription factor C/EBPα in mice. Mol Cell Biol 26: 1109–1123, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boggaram V. Regulation of surfactant protein gene expression by hyperoxia in the lung. Antioxid Redox Signal 6: 185–190, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bonikos DS, Bensch KG, Ludwin SK, Northway WH., Jr Oxygen toxicity in the newborn. The effect of prolonged 100% O2 exposure on the lungs of newborn mice. Lab Invest 32: 619–635, 1975 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

