Role of myosin light chain kinase in regulation of basal blood pressure and maintenance of salt-induced hypertension
- PMID: 21572007
- PMCID: PMC3154661
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01212.2010
Role of myosin light chain kinase in regulation of basal blood pressure and maintenance of salt-induced hypertension
Abstract
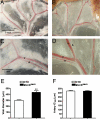
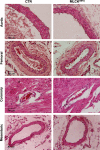
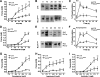
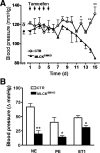
Vascular tone, an important determinant of systemic vascular resistance and thus blood pressure, is affected by vascular smooth muscle (VSM) contraction. Key signaling pathways for VSM contraction converge on phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain (RLC) of smooth muscle myosin. This phosphorylation is mediated by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) but Ca(2+)-independent kinases may also contribute, particularly in sustained contractions. Signaling through MLCK has been indirectly implicated in maintenance of basal blood pressure, whereas signaling through RhoA has been implicated in salt-induced hypertension. In this report, we analyzed mice with smooth muscle-specific knockout of MLCK. Mesenteric artery segments isolated from smooth muscle-specific MLCK knockout mice (MLCK(SMKO)) had a significantly reduced contractile response to KCl and vasoconstrictors. The kinase knockout also markedly reduced RLC phosphorylation and developed force. We suggest that MLCK and its phosphorylation of RLC are required for tonic VSM contraction. MLCK(SMKO) mice exhibit significantly lower basal blood pressure and weaker responses to vasopressors. The elevated blood pressure in salt-induced hypertension is reduced below normotensive levels after MLCK attenuation. These results suggest that MLCK is necessary for both physiological and pathological blood pressure. MLCK(SMKO) mice may be a useful model of vascular failure and hypotension.
Figures
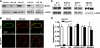

Similar articles
-
Enhanced contractility and myosin phosphorylation induced by Ca(2+)-independent MLCK activity in hypertensive rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jul 1;91(1):162-70. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr043. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21378385 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor κB kinase 2 is a myosin light chain kinase in vascular smooth muscle.Circ Res. 2013 Aug 16;113(5):562-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301510. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23817200 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin light chain kinase activation and calcium sensitization in smooth muscle in vivo.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):C358-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.90645.2007. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18524939 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin light chain kinase and the role of myosin light chain phosphorylation in skeletal muscle.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011 Jun 15;510(2):120-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.01.017. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21284933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain by myosin light chain kinase, and muscle contraction.Circ J. 2009 Feb;73(2):208-13. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-08-1041. Epub 2008 Dec 26. Circ J. 2009. PMID: 19110504 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct Roles of Smooth Muscle and Non-muscle Myosin Light Chain-Mediated Smooth Muscle Contraction.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 3;11:593966. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.593966. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33424621 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling to contractile proteins by muscarinic and purinergic pathways in neurally stimulated bladder smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;590(20):5107-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.235424. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22890701 Free PMC article.
-
ITRAQ-Based Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Effect of Neoliensinine on KCl-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction by Inhibiting Regulatory Light Chain Phosphorylation.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 11;10:979. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00979. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31572175 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic approaches to identify pathological limitations in aortic smooth muscle contraction.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 1;13(3):e0193769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193769. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29494672 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Licorice Functional Components Intakes on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and NETWORK Toxicology.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 2;16(21):3768. doi: 10.3390/nu16213768. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Sodium and potassium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. N Engl J Med 356: 1966–1978, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Chang Z, Zhang Q, Feng Q, Xu J, Teng T, Luan Q, Shan C, Hu Y, Hemmings BA, Gao X, Yang Z. Deletion of Akt1 causes heart defects and abnormal cardiomyocyte proliferation. Dev Biol 347: 384–391: - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW, Jr The genetic dissection of essential hypertension. Nat Rev Genet 7: 829–840, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Davis MJ, Hill MA. Signaling mechanisms underlying the vascular myogenic response. Physiol Rev 79: 387–423, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Davis MJ, Wu X, Nurkiewicz TR, Kawasaki J, Davis GE, Hill MA, Meininger GA. Integrins and mechanotransduction of the vascular myogenic response. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H1427–H1433, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

