Glutamate-induced calcium signals stimulate CO production in piglet astrocytes
- PMID: 21572018
- PMCID: PMC3154668
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01277.2010
Glutamate-induced calcium signals stimulate CO production in piglet astrocytes
Abstract
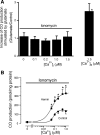
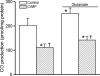
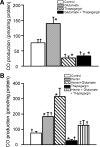
Glutamate-stimulated, astrocyte-derived carbon monoxide (CO) causes cerebral arteriole dilation by activating smooth muscle cell large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels. Here, we examined the hypothesis that glutamate activates heme oxygenase (HO)-2 and CO production via the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i))/Ca(2+)-calmodulin signaling pathway in newborn pig astrocytes. The major findings are: 1) glutamate stimulated Ca(2+) transients and increased steady-state [Ca(2+)](i) in cerebral cortical astrocytes in primary culture, 2) in astrocytes permeabilized with ionomycin, elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) concentration-dependently increased CO production, 3) glutamate did not affect CO production at any [Ca(2+)](i) when the [Ca(2+)](i) was held constant, 4) thapsigargin, a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase blocker, decreased basal CO production and blocked glutamate-induced increases in CO, and 5) calmidazolium, a calmodulin inhibitor, blocked CO production induced by glutamate and by [Ca(2+)](i) elevation. Taken together, our data are consistent with the hypothesis that glutamate elevates [Ca(2+)](i) in astrocytes, leading to Ca(2+)- and calmodulin-dependent HO-2 activation, and CO production.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glutamate regulates Ca2+ signals in smooth muscle cells of newborn piglet brain slice arterioles through astrocyte- and heme oxygenase-dependent mechanisms.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):H562-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00823.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19966053 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-derived CO is a diffusible messenger that mediates glutamate-induced cerebral arteriolar dilation by activating smooth muscle Cell KCa channels.Circ Res. 2008 Feb 1;102(2):234-41. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.164145. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 17991880 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon monoxide and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cerebral arteriolar responses to glutamate and hypoxia in newborn pigs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):H3193-200. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00274.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17766483 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of glutamate stimulation of CO production in cerebral microvessels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003 Jul;285(1):H74-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01081.2002. Epub 2003 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12623781
-
Neurointegrity and neurophysiology: astrocyte, glutamate, and carbon monoxide interactions.Med Gas Res. 2019 Jan-Mar;9(1):24-45. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.254639. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 30950417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional role of astrocyte glutamate receptors and carbon monoxide in cerebral vasodilation response to glutamate.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):H2257-66. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01011.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22467311 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte regulation of cerebral vascular tone.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Sep 1;305(5):H609-19. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00359.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23792684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of gasotransmitters in neonatal physiology.Nitric Oxide. 2020 Feb 1;95:29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Nitric Oxide. 2020. PMID: 31870965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte Bioenergetics and Major Psychiatric Disorders.Adv Neurobiol. 2021;26:173-227. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77375-5_9. Adv Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34888836 Review.
-
From unspecific to adjusted, how the BOLD response in the rat hippocampus develops during consecutive stimulations.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Feb;37(2):590-604. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16634715. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 26911895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkayed NJ, Birks EK, Hudetz AG, Roman RJ, Henderson L, Harder DR. Inhibition of brain P-450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase decreases baseline cerebral blood flow. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 271: H1541–H1546, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Birks EK, Narayanan J, Petrie KA, Kohler-Cabot AE, Harder DR. Role of P-450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase in the response of cerebral blood flow to glutamate in rats. Stroke 28: 1066–1072, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Narayanan J, Gebremedhin D, Medhora M, Roman RJ, Harder DR. Molecular characterization of an arachidonic acid epoxygenase in rat brain astrocytes. Stroke 27: 971–979, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Beck A, Nieden RZ, Schneider HP, Deitmer JW. Calcium release from intracellular stores in rodent astrocytes and neurons in situ. Cell Cal 35: 47–58, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bezzi P, Carmignoto G, Pasti L, Vesce S, Rossi D, Rizzini BL, Pozzan T, Volterra A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature 391: 281–285, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

