Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA
- PMID: 21572438
- PMCID: PMC3117022
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10006
Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA
Abstract
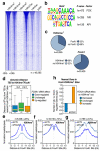
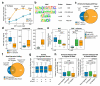
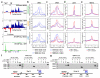
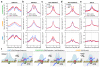
Mammalian genomes are populated with thousands of transcriptional enhancers that orchestrate cell-type-specific gene expression programs, but how those enhancers are exploited to institute alternative, signal-dependent transcriptional responses remains poorly understood. Here we present evidence that cell-lineage-specific factors, such as FoxA1, can simultaneously facilitate and restrict key regulated transcription factors, exemplified by the androgen receptor (AR), to act on structurally and functionally distinct classes of enhancer. Consequently, FoxA1 downregulation, an unfavourable prognostic sign in certain advanced prostate tumours, triggers dramatic reprogramming of the hormonal response by causing a massive switch in AR binding to a distinct cohort of pre-established enhancers. These enhancers are functional, as evidenced by the production of enhancer-templated non-coding RNA (eRNA) based on global nuclear run-on sequencing (GRO-seq) analysis, with a unique class apparently requiring no nucleosome remodelling to induce specific enhancer-promoter looping and gene activation. GRO-seq data also suggest that liganded AR induces both transcription initiation and elongation. Together, these findings reveal a large repository of active enhancers that can be dynamically tuned to elicit alternative gene expression programs, which may underlie many sequential gene expression events in development, cell differentiation and disease progression.
Figures
References
-
- Barski A, et al. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- HG004659/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK01847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM049369/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049369/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS34934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004659/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DK37949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

