Comparison of sublingual, vaginal, and oral misoprostol in cervical ripening for first trimester abortion
- PMID: 21572652
- PMCID: PMC3081456
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.77356
Comparison of sublingual, vaginal, and oral misoprostol in cervical ripening for first trimester abortion
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the effectiveness and tolerability of misoprostol as a cervical ripening agent in first trimester abortion through three different routes of administration before surgical evacuation (SE).
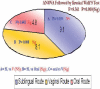
Materials and methods: It was a hospital based prospective randomized open labeled parallel study. A total of 150 randomly selected married women were divided in three groups for sublingual (S/L), vaginal and oral 400 μg of misoprostol single dose administration. The drug was administered 3-4 h before SE in the S/L and vaginal groups and 12 h before the procedure in the oral group. Efficacy was assessed on the basis of time taken for ripening, dilatation achieved, duration of the procedure, intra-operative blood loss, and pain score. The tolerability was noted on the basis of side effects.
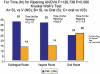
Results: The mean time taken for cervical ripening was less in sublingual administration (3.7±1.2 hr) as compared to the vaginal and oral routes. The S/L group had significant cervical dilatation (P<0.001) and the duration of SE was less as compared to the vaginal and oral routes. However, the mean intraoperative blood loss was more in sublingual as compared to the vaginal and oral groups. The intra-operative pain score of the S/L group was significantly lower (1.9±1.1, P<0.05) as compared to the vaginal (2.6±1.7) or oral route (3.3±1.7). Loose motions and nausea/vomiting were more with the S/L and oral routes while blood loss was more in the vaginal route.
Conclusion: Administration of misoprostol by the sublingual route is better than the oral and vaginal routes for cervical ripening.
Keywords: Cervical ripening; first trimester abortion; misoprostol; surgical evacuation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Niinimäki M, Jouppila P, Martikainen H, Talvensaari-Mattila A. A randomized study comparing efficacy and patient satisfaction in medical or surgical treatment of miscarriage. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:367–72. - PubMed
-
- Kulier R, Gülmezoglu AM, Hofmeyr GJ, Cheng LN, Campana A. Medical methods for first trimester abortion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2:CD002855. - PubMed
-
- Saxena P, Salhan S, Sarda N. Sublingual versus vaginal route of misoprostol for cervical ripening prior to surgical termination of first trimester abortions. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006;125:109–13. - PubMed
-
- Caliskan E, Filiz T, Yucesoy G, Coskun E, Vural B, Corakci A. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening PRIOR TO manual vacuum aspiration under local anaesthesia: A randomized study. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2007;12:372–7. - PubMed
-
- Lawrie A, Penney G, Templeton A. A randomised comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for cervical priming before suction termination of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;103:1117–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources