Nevus depigmentosus treated by melanocyte-keratinocyte transplantation
- PMID: 21572678
- PMCID: PMC3081481
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2077.79185
Nevus depigmentosus treated by melanocyte-keratinocyte transplantation
Abstract
Background: Nevus depigmentosus is a congenital, nonprogressive hypopigmented disorder. Various therapeutic methods have been attempted to repigment nevus with variable results.
Objective: The objective of this study is to report our experience of treatment of nevus depigmentosus with a combination of noncultured melanocyte-keratinocyte transplantation (MKTP) and excimer laser sessions.
Materials and methods: Six patients (male 1, female 5) of nevus depigmentosus were treated with a combination of noncultured melanocyte-keratinocyte transplantation and excimer laser. One patient was lost to follow-up. Remaining five patients were observed for a period ranging from 7 to 30 months.
Results: Two patients responded poorly to MKTP. The remaining three patients responded with repigmentation ranging from 80% to 100% but the quality of repigmentation was unsatisfactory in two of them.
Conclusion: Though repigmentation of nevus depigmentosus is possible by grafting techniques, the results are inconsistent and recurrence is possible.
Keywords: Grafting; melanocyte transplantation; nevus; nevus depigmentosus; nevus treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
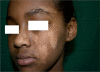


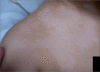

References
-
- Lernia VD. Segmental nevus depigmentosus: Analysis of 120 patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:349–53. - PubMed
-
- Coupe RL. Unilateral systematized achromic nevus. Dermatologica. 1976;134:19–35. - PubMed
-
- Pinto FJ, Bolognia JL. Disorders of hypopigmentation in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1991;38:991–1017. - PubMed
-
- Jimbow K, Fitzpatrick TB, Szabo G, Hori Y. Congenital circumscribed hypomelanosis: A characterization based on electron microscopic study of tuberous sclerosis, nevus depigmentosus and piebaldism. J Invest Dermatol. 1975;64:50–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee HS, Chun YS, Hann SK. Nevus depigmentosus: Clinical features and histopathologic characteristics in 67 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:21–6. - PubMed

