Pulmonary vascular complications of chronic liver disease: Pathophysiology, imaging, and treatment
- PMID: 21572693
- PMCID: PMC3081557
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.78412
Pulmonary vascular complications of chronic liver disease: Pathophysiology, imaging, and treatment
Abstract
To review the pathogenesis of pulmonary vascular complications of liver disease, we discuss their clinical implications, and therapeutic considerations, with emphasis on potential reversibility of the hepatopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation. In this review, we also discuss the role of imaging in pulmonary vascular complications associated with liver disease.
Keywords: Hepatopulmonary syndrome; Yttrium-90 microsphere embolization hepatocellular carcinoma; portopulmonary hypertension; pulmonary arteriovenous shunts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




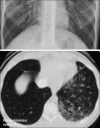
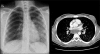



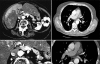
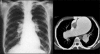
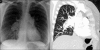
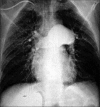
References
-
- Krowka MJ, Cortese DA. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: An evolving perspective in the era of liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1990;11:138–42. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy TC, Knudson RJ. Exercise-aggravated hypoxemia and orthodexia in cirrhosis. Chest. 1997;72:305–9. - PubMed
-
- Krowka MJ, Cortese DA. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: Current concepts in diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Chest. 1994;105:1528–37. - PubMed
-
- Abrams GA, Jaffe CC, Hoffer PB, Binder HJ, Fallon MB. Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1283–8. - PubMed
-
- Castro M, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: A pulmonary vascular complication of liver disease. Clin Chest Med. 1996;17:35–48. - PubMed

