Hydrogen sulfide attenuated tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammatory signaling and dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 21572963
- PMCID: PMC3091882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019766
Hydrogen sulfide attenuated tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammatory signaling and dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuated Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Inflammatory Signaling and Dysfunction in Vascular Endothelial Cells.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 1;19(10):e0311557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311557. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39352903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S), the third physiologically relevant gaseous molecule, is recognized increasingly as an anti-inflammatory mediator in various inflammatory conditions. Herein, we explored the effects and mechanisms of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS, a H(2)S donor) on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) dysfunction.
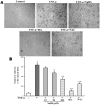
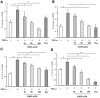
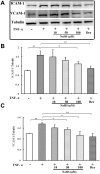
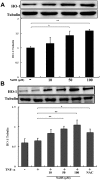
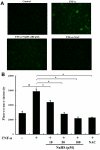
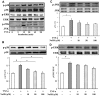
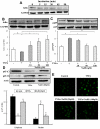
Methodology and principal findings: Application of NaHS concentration-dependently suppressed TNF-α-induced mRNA and proteins expressions of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), mRNA expression of P-selectin and E-selectin as well as U937 monocytes adhesion to HUVEC. Western blot analysis revealed that the expression of the cytoprotective enzyme, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), was induced and coincident with the anti-inflammatory action of NaHS. Furthermore, TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation assessed by IκBα degradation and p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation and ROS production were diminished in cells subjected to treatment with NaHS.
Significance: H(2)S can exert an anti-inflammatory effect in endothelial cells through a mechanism that involves the up-regulation of HO-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Szmitko PE, Wang CH, Weisel RD, Jeffries GA, Anderson TJ, et al. Biomarkers of vascular disease linking inflammation to endothelial activation: Part II. Circulation. 2003;108:2041–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

