Protection of neurons in the retinal ganglion cell layer against excitotoxicity by the N-acylethanolamine, N-linoleoylethanolamine
- PMID: 21573043
- PMCID: PMC3090310
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S18309
Protection of neurons in the retinal ganglion cell layer against excitotoxicity by the N-acylethanolamine, N-linoleoylethanolamine
Abstract
Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases and disease processes of the eye, including glaucoma. The protection of RGCs has been an important strategy for combating glaucoma, but little clinical success has been reported to date. One pathophysiological consequence of glaucoma is excessive extracellular glutamate subsequently leading to excitotoxicity in the retina. Endocannabinoids, such as the N-acylethanolamine (NAE), arachidonylethanolamine (NAE 20:4), exhibit neuroprotective properties in some models of neurodegenerative disease. The majority of NAEs, however, are not cannabinoids, and their physiological function is not clear. Here, we determined whether the noncannabinoid NAE, linoleoylethanolamine (NAE18:2), protects neurons in the RGC layer against glutamate excitotoxicity in ex-vivo retina cultures. Using a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP (2'-deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate) nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay, we determined that NAE18:2 reduces the number of apoptotic RGC layer neurons in response to glutamate and conclude that NAE18:2 is a neuroprotective compound with potential for treating glaucomatous retinopathy.
Keywords: calcium signaling; eye; glaucoma; glutamate; immunocytochemistry; neuroprotection; vision.
Figures
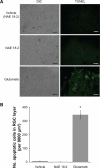
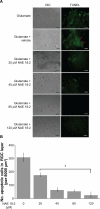

References
-
- Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet. 2004;363:1711–1720. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, Neufeld AH. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a potentially neurodestructive cytokine produced by glia in the human glaucomatous optic nerve head. Glia. 2000;32:42–50. - PubMed
-
- Moreno MC, Campanelli J, Sande P, Sánez DA, Keller Sarmiento MI, Rosenstein RE. Retinal oxidative stress induced by high intraocular pressure. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:803–812. - PubMed
-
- Seki M, Lipton SA. Targeting excitotoxic/free radical signaling pathways for therapeutic intervention in glaucoma. Prog Brain Res. 2008;173:495–510. - PubMed
-
- Hare WA, Wheeler L. Experimental glutamatergic excitotoxicity in rabbit retinal ganglion cells: block by memantine. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:2940–2948. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

