Elevated miR-499 levels blunt the cardiac stress response
- PMID: 21573063
- PMCID: PMC3090396
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019481
Elevated miR-499 levels blunt the cardiac stress response
Abstract
Background: The heart responds to myriad stresses by well-described transcriptional responses that involve long-term changes in gene expression as well as more immediate, transient adaptations. MicroRNAs quantitatively regulate mRNAs and thus may affect the cardiac transcriptional output and cardiac function. Here we investigate miR-499, a microRNA embedded within a ventricular-specific myosin heavy chain gene, which is expressed in heart and skeletal muscle.
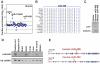
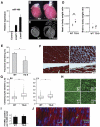
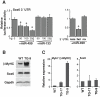
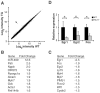
Methodology/principal findings: We assessed miR-499 expression in human tissue to confirm its potential relevance to human cardiac gene regulation. Using a transgenic mouse model, we found that elevated miR-499 levels caused cellular hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction in a dose-dependent manner. Global gene expression profiling revealed altered levels of the immediate early stress response genes (Egr1, Egr2 and Fos), ß-myosin heavy chain (Myh7), and skeletal muscle actin (Acta1). We verified the effect of miR-499 on the immediate early response genes by miR-499 gain- and loss-of-function in vitro. Consistent with a role for miR-499 in blunting the response to cardiac stress, asymptomatic miR-499-expressing mice had an impaired response to pressure overload and accentuated cardiac dysfunction.
Conclusions: Elevated miR-499 levels affect cardiac gene expression and predispose to cardiac stress-induced dysfunction. miR-499 may titrate the cardiac response to stress in part by regulating the immediate early gene response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Liew CC, Dzau VJ. Molecular genetics and genomics of heart failure. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:811–825. - PubMed
-
- Nabel EG. Cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:60–72. - PubMed
-
- Lowes BD, Gilbert EM, Abraham WT, Minobe WA, Larrabee P, et al. Myocardial gene expression in dilated cardiomyopathy treated with beta-blocking agents. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1357–1365. - PubMed
-
- Kaab S, Barth AS, Margerie D, Dugas M, Gebauer M, et al. Global gene expression in human myocardium-oligonucleotide microarray analysis of regional diversity and transcriptional regulation in heart failure. J Mol Med. 2004;82:308–316. - PubMed
-
- Hwang JJ, Allen PD, Tseng GC, Lam CW, Fananapazir L, et al. Microarray gene expression profiles in dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathic end-stage heart failure. Physiol Genomics. 2002;10:31–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

