Specificity of mimotope-induced anti-high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen (HMW-MAA) antibodies does not ensure biological activity
- PMID: 21573118
- PMCID: PMC3089623
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019383
Specificity of mimotope-induced anti-high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen (HMW-MAA) antibodies does not ensure biological activity
Abstract
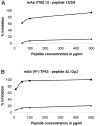
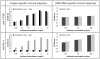
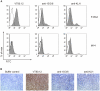
Vaccines based on peptide mimics (mimotopes) of conformational tumor antigen epitopes have been investigated for a variety of human tumors including breast cancer, tumors expressing the carcinoembryonic antigen, B cell lymphoma, neuroblastoma, and melanoma. In our previous work, we designed a vaccine based on a mimotope of the high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen (HMW-MAA) that elicited HMW-MAA-specific antibodies (Abs) with anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo. In this study, we aimed to identify mimotopes of additional distinct HMW-MAA epitopes, since they could be used to construct a polymimotope melanoma vaccine. For this purpose, random peptide phage libraries were screened with the anti-HMW-MAA monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) VT80.12 and VF1-TP43 yielding one peptide ligand for each mAb. Both peptides inhibited the binding of the corresponding mAb to the HMW-MAA. Furthermore, when coupled to the carrier protein keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH), both HMW-MAA mimotopes elicited peptide-specific Abs in rabbits or BALB/c mice, but only the mimotope isolated with the mAb VT80.12 elicited HMW-MAA-specific Abs and only in mice. However, the latter Abs had no detectable effect on HMW-MAA expressing human melanoma cells in vitro. These results describe limitations related to the phage display technique and emphasize the need to characterize the functional properties of the mAb utilized to isolate mimotopes of the corresponding epitopes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
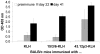

Similar articles
-
Cross-reactivity of mimotopes with a monoclonal antibody against the high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen (HMW-MAA) does not predict cross-reactive immunogenicity.Melanoma Res. 2005 Apr;15(2):111-7. doi: 10.1097/00008390-200504000-00005. Melanoma Res. 2005. PMID: 15846144
-
High-molecular-weight melanoma-associated antigen mimotope immunizations induce antibodies recognizing melanoma cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005 Jul;54(7):677-84. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0632-7. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. PMID: 15565329 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting melanoma cells with human high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen-specific antibodies elicited by a peptide mimotope: functional effects.J Immunol. 2006 May 15;176(10):6046-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.6046. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16670313
-
Immunotherapy of melanoma targeting human high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen: potential role of nonimmunological mechanisms.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1028:340-50. doi: 10.1196/annals.1322.040. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15650259 Review.
-
Human high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen mimicry by mouse anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies MK2-23. Experimental studies and clinical trials in patients with malignant melanoma.Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Feb-Mar;57(2-3):259-90. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90058-l. Pharmacol Ther. 1993. PMID: 8361995 Review.
Cited by
-
Phages bearing affinity peptides to bovine rotavirus differentiate the virus from other viruses.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028667. Epub 2011 Dec 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22163050 Free PMC article.
-
The development of inovirus-associated vector vaccines using phage-display technologies.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019 Sep;18(9):913-920. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2019.1651649. Epub 2019 Sep 8. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019. PMID: 31373843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage display for identifying peptides that bind the spike protein of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and possess diagnostic potential.Virus Genes. 2015 Aug;51(1):51-6. doi: 10.1007/s11262-015-1208-7. Epub 2015 May 27. Virus Genes. 2015. PMID: 26013256 Free PMC article.
-
Architectural insight into inovirus-associated vectors (IAVs) and development of IAV-based vaccines inducing humoral and cellular responses: implications in HIV-1 vaccines.Viruses. 2014 Dec 17;6(12):5047-76. doi: 10.3390/v6125047. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25525909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD20-Mimotope Peptides: A Model to Define the Molecular Basis of Epitope Spreading.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 18;20(8):1920. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081920. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31003532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campoli MR, Chang CC, Kageshita T, Wang X, McCarthy JB, et al. Human high molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen (HMW-MAA): a melanoma cell surface chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MSCP) with biological and clinical significance. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004;24:267–296. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wang Y, Yu L, Sakakura K, Visus C, et al. CSPG4 in cancer: multiple roles. Curr Mol Med. 2010;10:419–429. - PubMed
-
- Chang CC, Campoli M, Luo W, Zhao W, Zaenker KS, et al. Immunotherapy of melanoma targeting human high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen: potential role of nonimmunological mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1028:340–350. - PubMed
-
- Mittelman A, Chen ZJ, Liu CC, Hirai S, Ferrone S. Kinetics of the immune response and regression of metastatic lesions following development of humoral anti-high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen immunity in three patients with advanced malignant melanoma immunized with mouse antiidiotypic monoclonal antibody MK2-23. Cancer Res. 1994;54:415–421. - PubMed
-
- Mittelman A, Chen ZJ, Yang H, Wong GY, Ferrone S. Human high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen (HMW-MAA) mimicry by mouse anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody MK2-23: induction of humoral anti-HMW-MAA immunity and prolongation of survival in patients with stage IV melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:466–470. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

