Olfactory and visuospatial learning and memory performance in two strains of Alzheimer's disease model mice--a longitudinal study
- PMID: 21573167
- PMCID: PMC3088679
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019567
Olfactory and visuospatial learning and memory performance in two strains of Alzheimer's disease model mice--a longitudinal study
Abstract
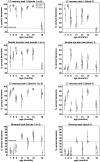
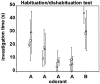
Using a longitudinal study design, two strains of Alzheimer's disease (AD) model mice, one expressing β-amyloid plaques and one expressing Tau protein-associated neurofibrillary tangles were assessed for olfactory and visuospatial learning and memory and their performance compared to that of age-matched controls. No significant difference between AD and control mice was found in the initial set of olfactory tasks performed at 6 months of age whereas both strains of AD mice performed significantly poorer than the controls in visuospatial learning at this age. Subsequent tests performed on the same individual animals at 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 15, and 18 months of age also failed to find systematic differences in olfactory performance between AD and control mice. In contrast, the AD mice performed consistently poorer than the controls in visuospatial re-learning tests performed at these ages. With most olfactory tasks, both AD and control mice displayed a marked decrease in performance between testing at 15 and 18 months of age. These results show that the two strains of AD model mice do not display an olfactory impairment in a time course consistent with human AD, but are impaired in visuospatial capabilities. The marked age-related changes observed with the olfactory tasks in both AD and control mice suggest that the observed lack of an AD-related olfactory impairment is not due to an insensitivity of the tests employed. Rather, they suggest that the olfactory system of the two AD mouse model strains may be surprisingly robust against AD-typical neuropathologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


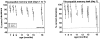
References
-
- Wilcock DM. The usefulness and challenges of transgenic mouse models in the study of Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol Disord. 2010;9:386–394. - PubMed
-
- Andorfer C, Kress Y, Espinoza M, de Silva R, Tucker KL, et al. Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J Neurochem. 2003;86:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Jankowsky JL, Fadale DJ, Anderson J, Xu GM, Gonzales V, et al. Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of the 42 residue beta-amyloid peptide in vivo: evidence for augmentation of a 42-specific gamma secretase. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:159–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

