Detection of head-to-tail DNA sequences of human bocavirus in clinical samples
- PMID: 21573237
- PMCID: PMC3087758
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019457
Detection of head-to-tail DNA sequences of human bocavirus in clinical samples
Abstract
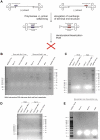
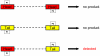
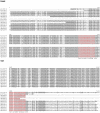
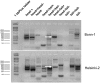
Parvoviruses are single stranded DNA viruses that replicate in a so called "rolling-hairpin" mechanism, a variant of the rolling circle replication known for bacteriophages like φX174. The replication intermediates of parvoviruses thus are concatemers of head-to-head or tail-to-tail structure. Surprisingly, in case of the novel human bocavirus, neither head-to-head nor tail-to-tail DNA sequences were detected in clinical isolates; in contrast head-to-tail DNA sequences were identified by PCR and sequencing. Thereby, the head-to-tail sequences were linked by a novel sequence of 54 bp of which 20 bp also occur as conserved structures of the palindromic ends of parvovirus MVC which in turn is a close relative to human bocavirus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tattersall P. Kerr JRB, M.E., Cotmore S, editors. The evolution of Parvovirus Taxonomy. 2006. pp. 5–14.
-
- Tattersall P, Ward DC. Rolling hairpin model for replication of parvovirus and linear chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1976;263:106–109. - PubMed
-
- Hirt B. Molecular biology of autonomous parvoviruses. Contrib Microbiol. 2000;4:163–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

