Predictive factors of urinary tract infections among the oldest old in the general population. A population-based prospective follow-up study
- PMID: 21575195
- PMCID: PMC3117726
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-57
Predictive factors of urinary tract infections among the oldest old in the general population. A population-based prospective follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infections (UTI) are common among the oldest old and may lead to a few days of illness, delirium or even to death. We studied the incidence and predictive factors of UTI among the oldest old in the general population.
Methods: The Leiden 85-plus Study is a population-based prospective follow-up study of 86-year-old subjects in Leiden, The Netherlands. Information on the diagnosis of UTI was obtained annually during four years of follow-up from the medical records and interviews of treating physicians. A total of 157 men and 322 women aged 86 years participated in the study. Possible predictive factors were collected at baseline, including history of UTI between the age of 85 and 86 years, aspects of functioning (cognitive impairment (Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) < 19), presence of depressive symptoms (Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) > 4), disability in activities of daily living (ADL)), and co-morbidities.
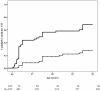
Results: The incidence of UTI from age 86 through 90 years was 11.2 (95% confidence interval (CI) 9.4, 13.1) per 100 person-years at risk. Multivariate analysis showed that history of UTI between the age of 85 and 86 years (hazard ratio (HR) 3.4 (95% CI 2.4, 5.0)), impaired cognitive function (HR 1.9 (95% CI 1.3, 2.9)), disability in daily living (HR 1.7 (95% CI 1.1, 2.5)) and urine incontinence (HR 1.5 (95% CI 1.0, 2.1)) were independent predictors of an increased incidence of UTI from age 86 onwards.
Conclusions: Within the oldest old, a history of UTI between the age of 85 and 86 years, cognitive impairment, ADL disability and urine incontinence are independent predictors of developing UTI. These predictive factors could be used to target preventive measures to the oldest old at high risk of UTI.
Figures
References
-
- Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am J Med. 2002;113:5S–13S. - PubMed
-
- Ruben FL, Dearwater SR, Norden CW, Kuller LH, Gartner K, Shally A, Warshafsky G, Kelsey SF, O'Donnell C, Means E. Clinical infections in the noninstitutionalized geriatric age group: methods utilized and incidence of infections. The Pittsburgh Good Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:145–157. - PubMed
-
- RIVM. Acute urineweginfecties. Omvang van het probleem. Incidentie en sterfte naar leeftijd en geslacht [Acute urinary tract infections. Extent of the problem. Incidence and mortality by age and gender] (online) http://www.nationaalkompas.nl/gezondheid-en-ziekte/ziekten-en-aandoening...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

