Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer
- PMID: 21575859
- PMCID: PMC3142785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.008
Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer
Abstract
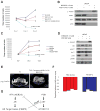
Prostate cancer is characterized by its dependence on androgen receptor (AR) and frequent activation of PI3K signaling. We find that AR transcriptional output is decreased in human and murine tumors with PTEN deletion and that PI3K pathway inhibition activates AR signaling by relieving feedback inhibition of HER kinases. Similarly, AR inhibition activates AKT signaling by reducing levels of the AKT phosphatase PHLPP. Thus, these two oncogenic pathways cross-regulate each other by reciprocal feedback. Inhibition of one activates the other, thereby maintaining tumor cell survival. However, combined pharmacologic inhibition of PI3K and AR signaling caused near-complete prostate cancer regressions in a Pten-deficient murine prostate cancer model and in human prostate cancer xenografts, indicating that both pathways coordinately support survival.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
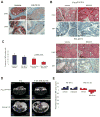
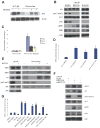
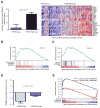
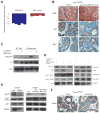
References
-
- Brachmann SM, Hofmann I, Schnell C, Fritsch C, Wee S, Lane H, Wang S, Garcia-Echeverria C, Maira SM. Specific apoptosis induction by the dual PI3K/mTor inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in HER2 amplified and PIK3CA mutant breast cancer cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106:22299–22304. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

