Attenuated nephritis in inducible nitric oxide synthase knockout C57BL/6 mice and pulmonary hemorrhage in CB17 SCID and recombination activating gene 1 knockout C57BL/6 mice infected with Leptospira interrogans
- PMID: 21576342
- PMCID: PMC3191955
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05099-11
Attenuated nephritis in inducible nitric oxide synthase knockout C57BL/6 mice and pulmonary hemorrhage in CB17 SCID and recombination activating gene 1 knockout C57BL/6 mice infected with Leptospira interrogans
Abstract
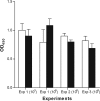
The aims of this study were to investigate the frequency of pulmonary hemorrhage (PH) in mice unable to produce functional B and T lymphocytes and to explore the effect of an inducible nitric oxide synthase gene (Inos) knockout (KO) on the frequency/severity of interstitial nephritis in vivo. We studied the outcome of infection by the virulent Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni strain Cop. The animals used were Inos KO mice, recombination activating gene 1 (Rag1) KO mice, CB17 severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice, and the respective wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 and BALB/c controls. The Inos KO and WT mice survived with no clinical symptoms of leptospirosis. The frequency and severity of nephritis was significantly lower in the Inos KO mice. All of the Rag1 KO and SCID animals died of acute leptospirosis, whereas all of the WT mice survived. PH was observed in 57 and 94% of Rag1 KO mice and in 83 and 100% of SCID mice, using inoculum doses of 10(7) and 10(6) leptospires, respectively. There was no evidence of PH in the WT controls. In conclusion, the loss of the Inos gene had a negligible effect on the outcome of leptospiral infection, although we observed a reduced susceptibility for interstitial nephritis in this group. Of note, the absence of functional B- and T-cell lymphocytes did not preclude the occurrence of PH. These data provide evidence that PH in leptospirosis may not be related only to autoimmune mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Adler B., de la Pena Moctezuma A. 2010. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Vet. Microbiol. 140:287–296 - PubMed
-
- Athanazio D. A., Santos C. S., Santos A. C., McBride F. W. C., Reis M. G. 2008. Experimental infection in tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma and interleukin 4 deficient mice by pathogenic Leptospira interrogans. Acta Trop. 105:95–98 - PubMed
-
- Athanazio D. A., et al. 2008. Rattus norvegicus as a model for persistent renal colonization by pathogenic Leptospira interrogans. Acta Trop. 105:176–180 - PubMed
-
- Cerqueira T. B., Athanazio D. A., Spichler A. S., Seguro A. C. 2008. Renal involvement in leptospirosis—new insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 12:248–252 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

